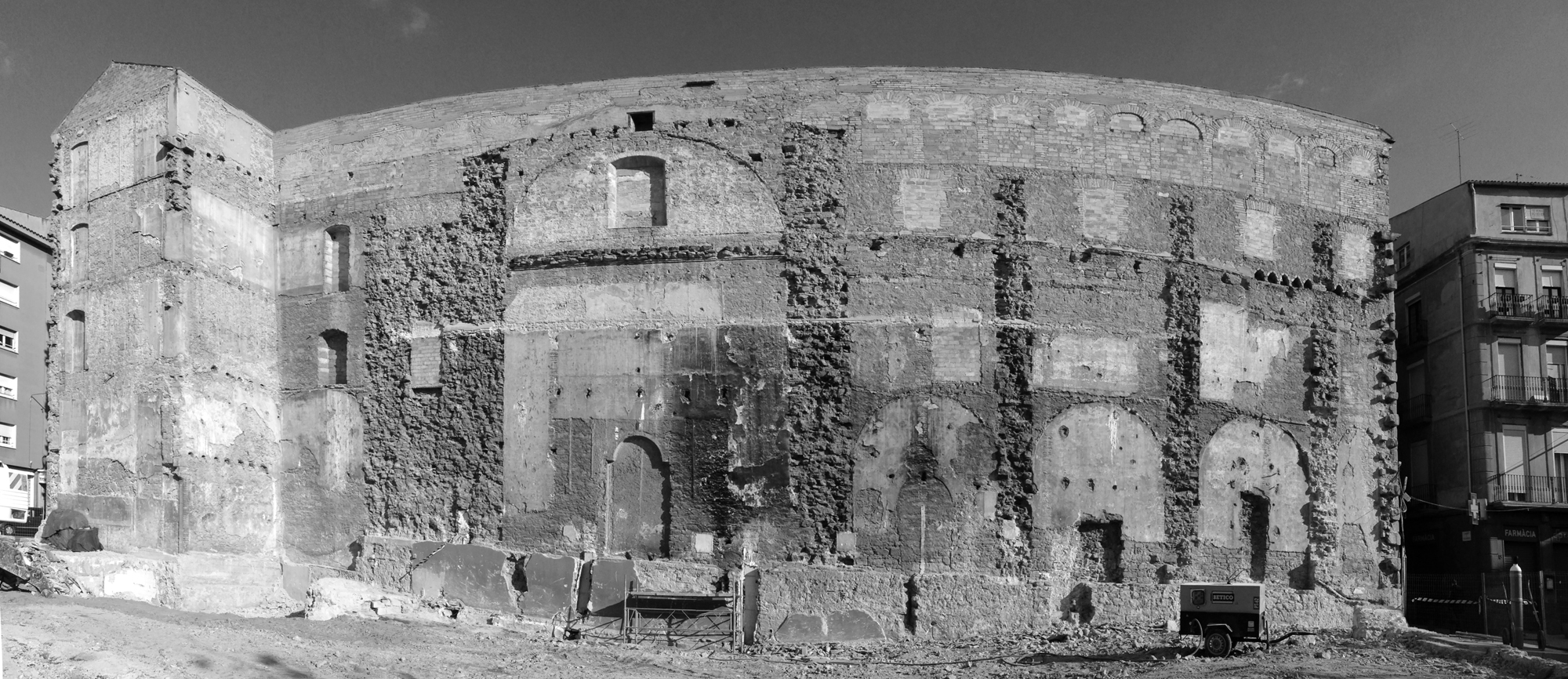
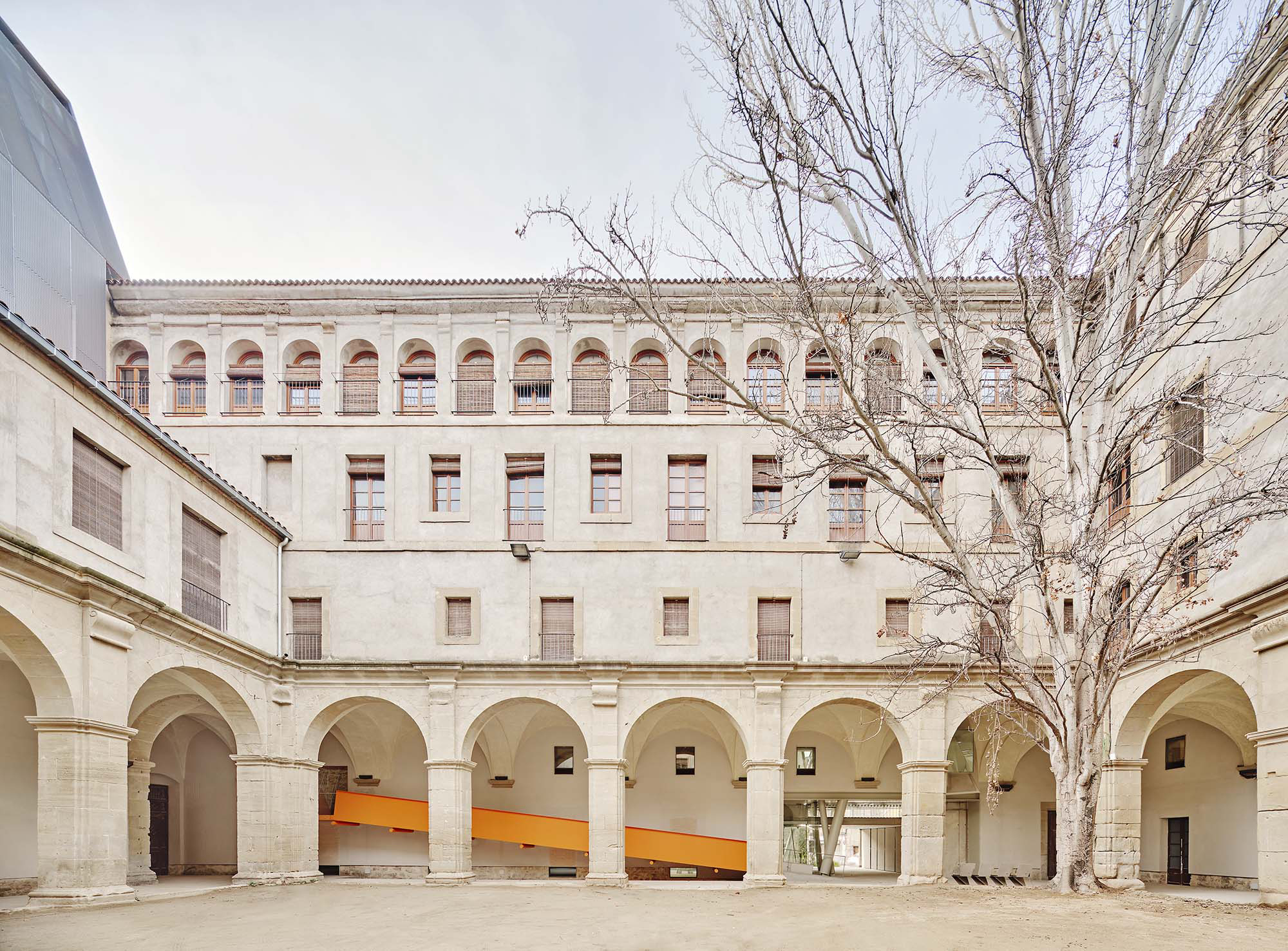
Sometimes surprising coincidences might occur. Between 2003 and 2011 we conducted the architectural intervention on Sant Francesc Convent , in Santpedor, to transform it into an auditorium. The project was carried out on a former convent built in the 18th century where only the church was remaining; the conventual wings and cloister had disappeared. Five years later, located in Manresa, we were commissioned to develop an inverse assignment from the previous one: an intervention on the Old Saint Ignatius College, a former religious complex based on a convent structure whose baroque church was demolished; only the wings of the old Jesuit college placed around a cloister remained. In both cases, the architectonical intervention was done on buildings amputated of one of its two essential elements; in the present project, the old baroque church.
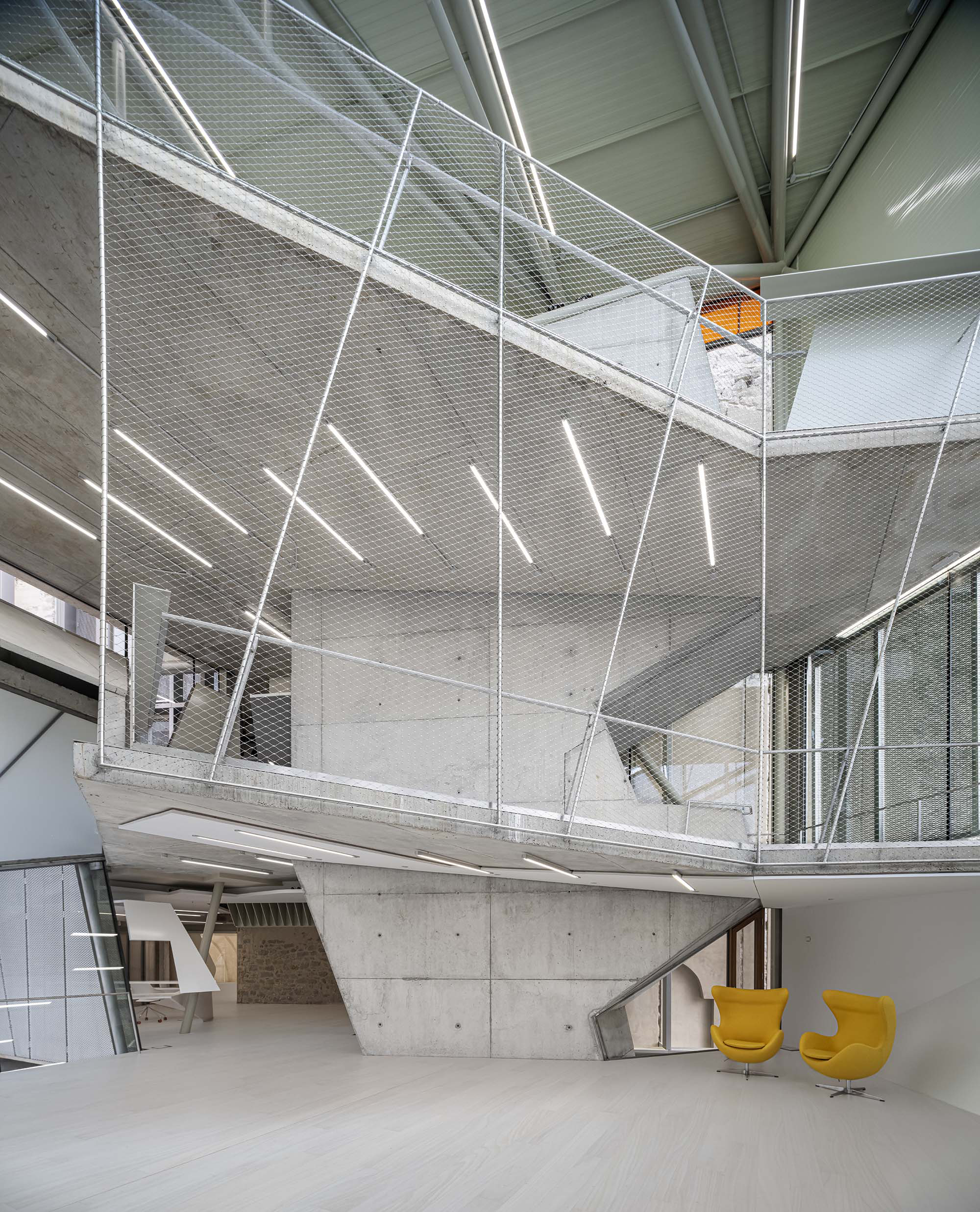
The construction of the new accesses to the old Jesuit college is framed in the global renovation project of the entire built complex, which should grant to rationalize, refresh, and rethink the spaces of the preexisting museum. The planned interventions should allow the building to host Baroque Museum of Catalonia and Manresa’s City History Museum.
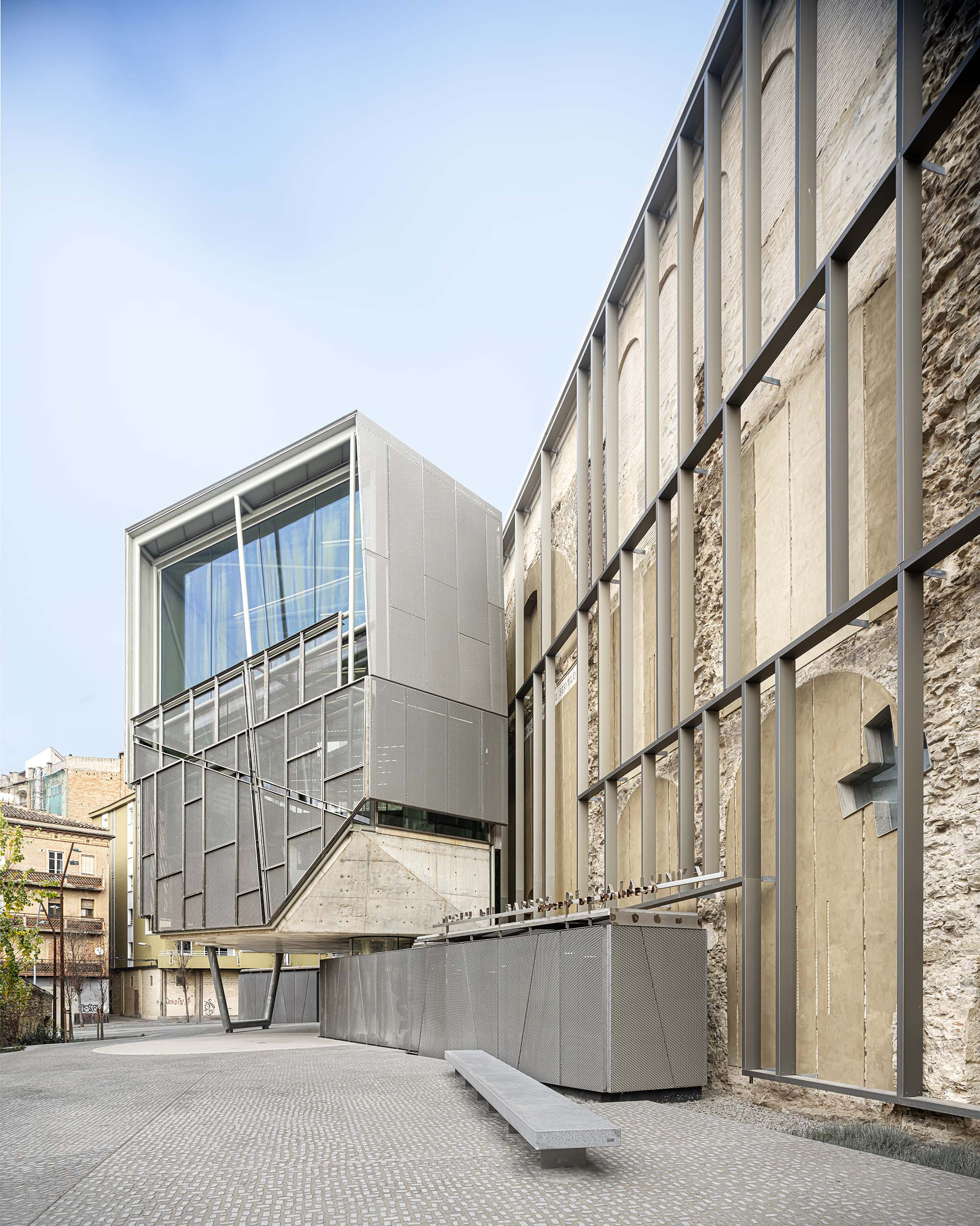
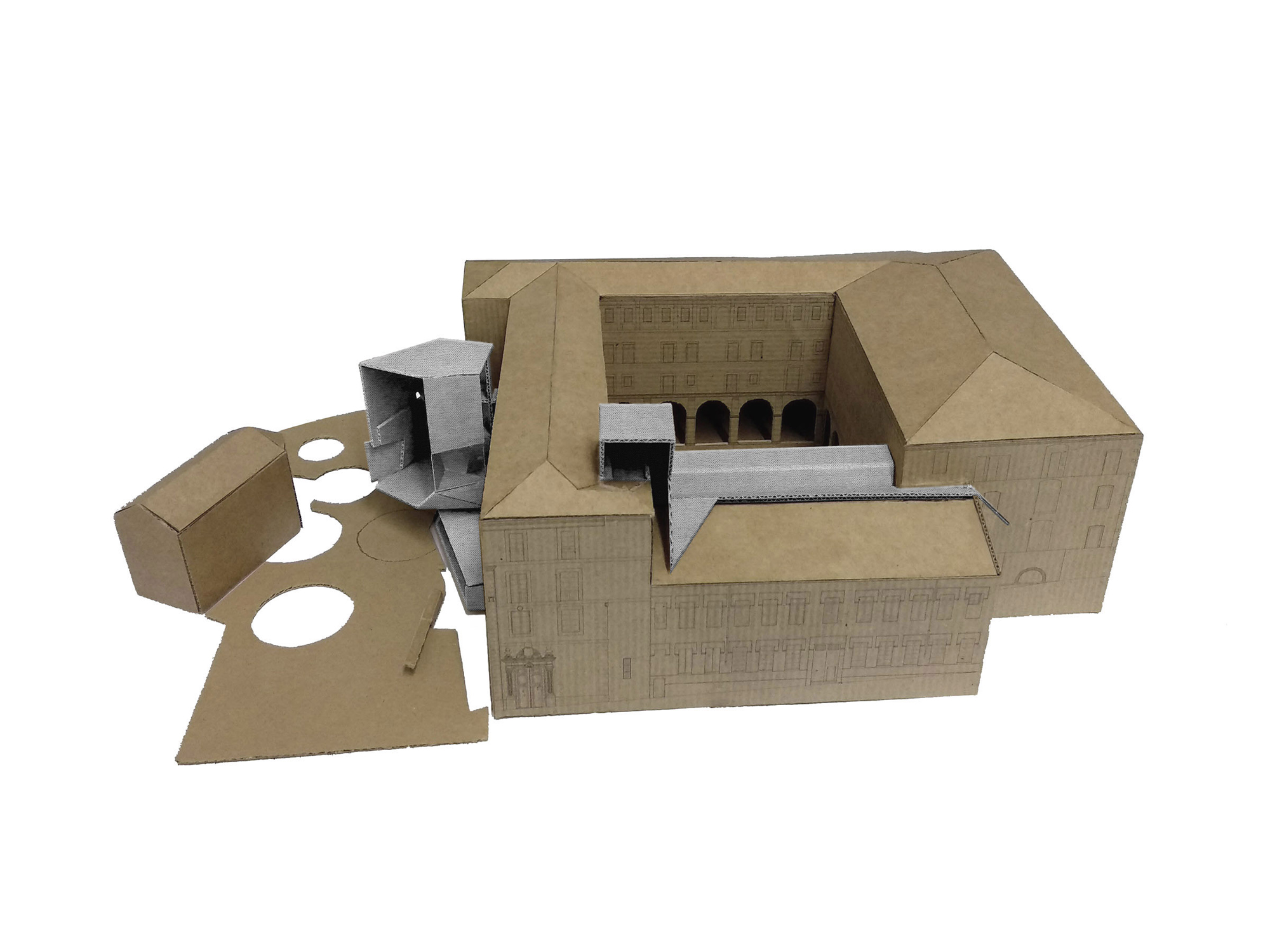
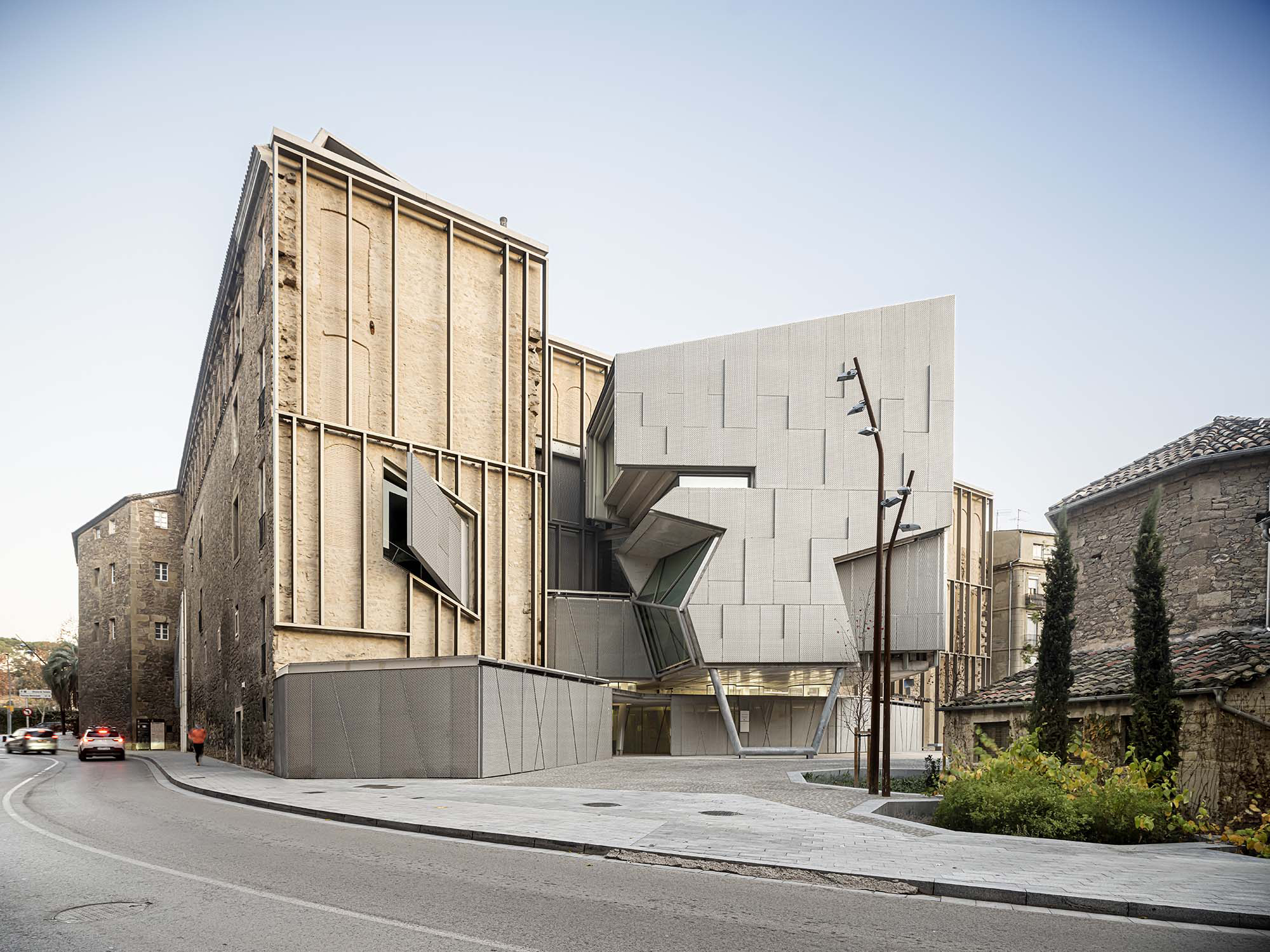
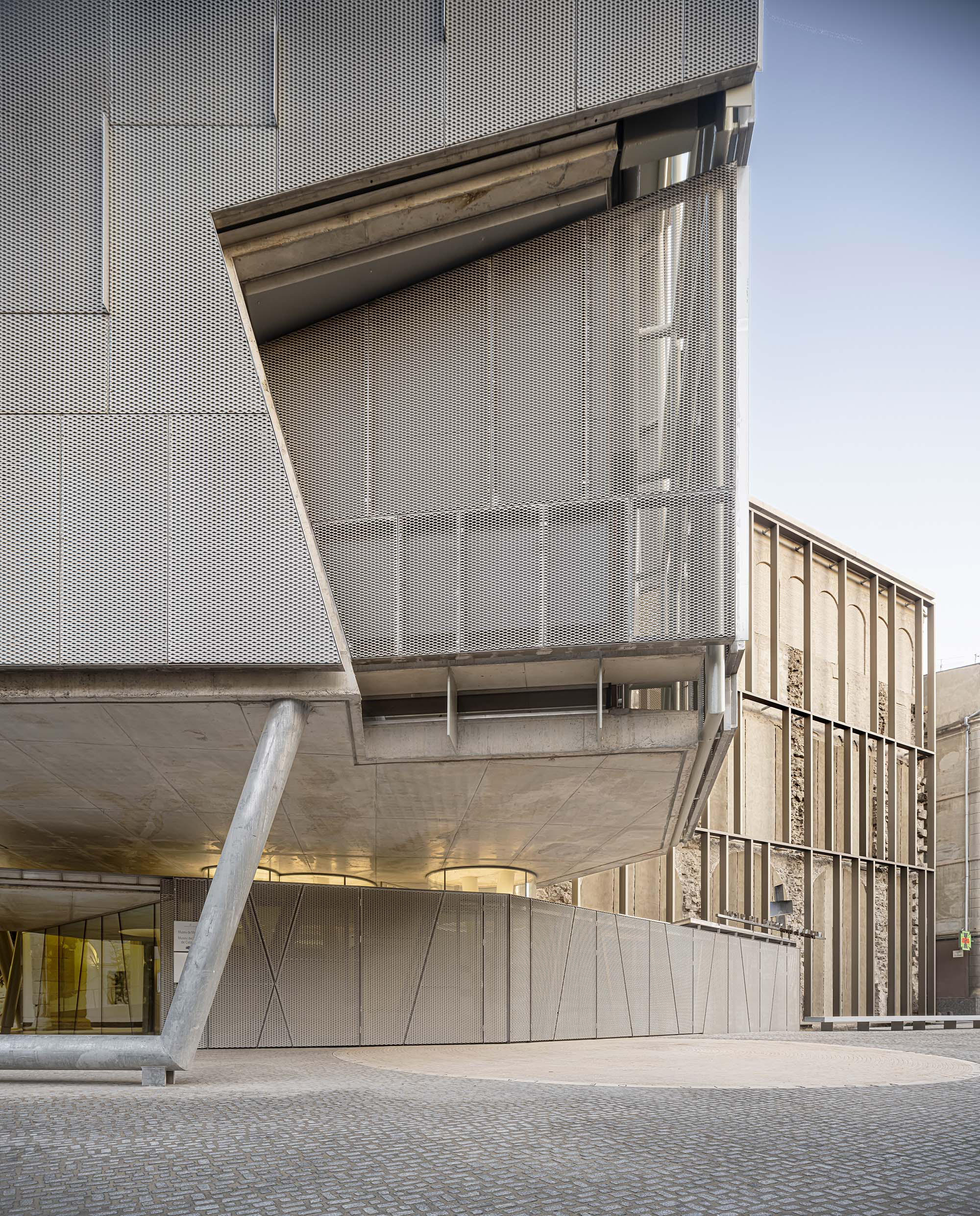
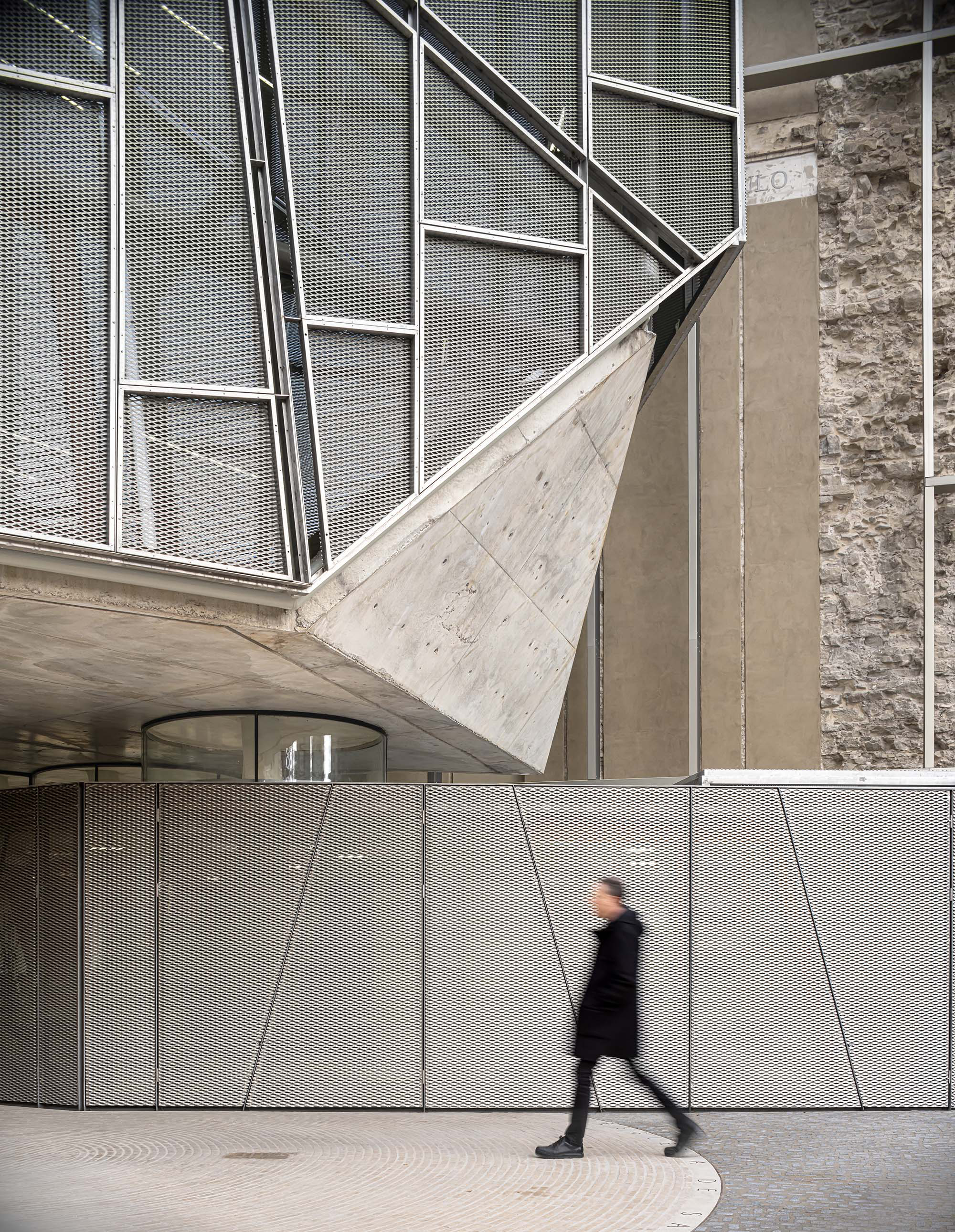
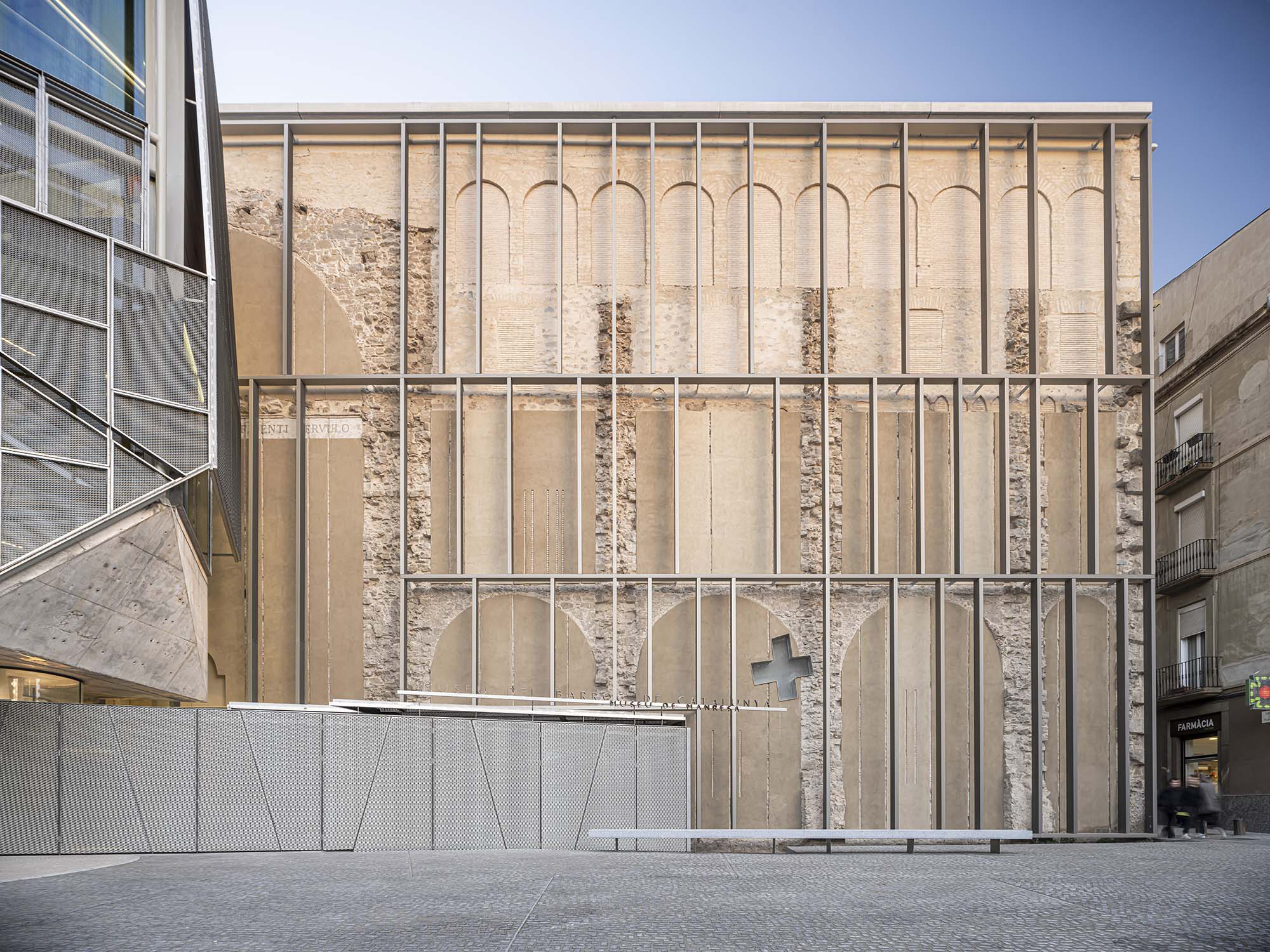
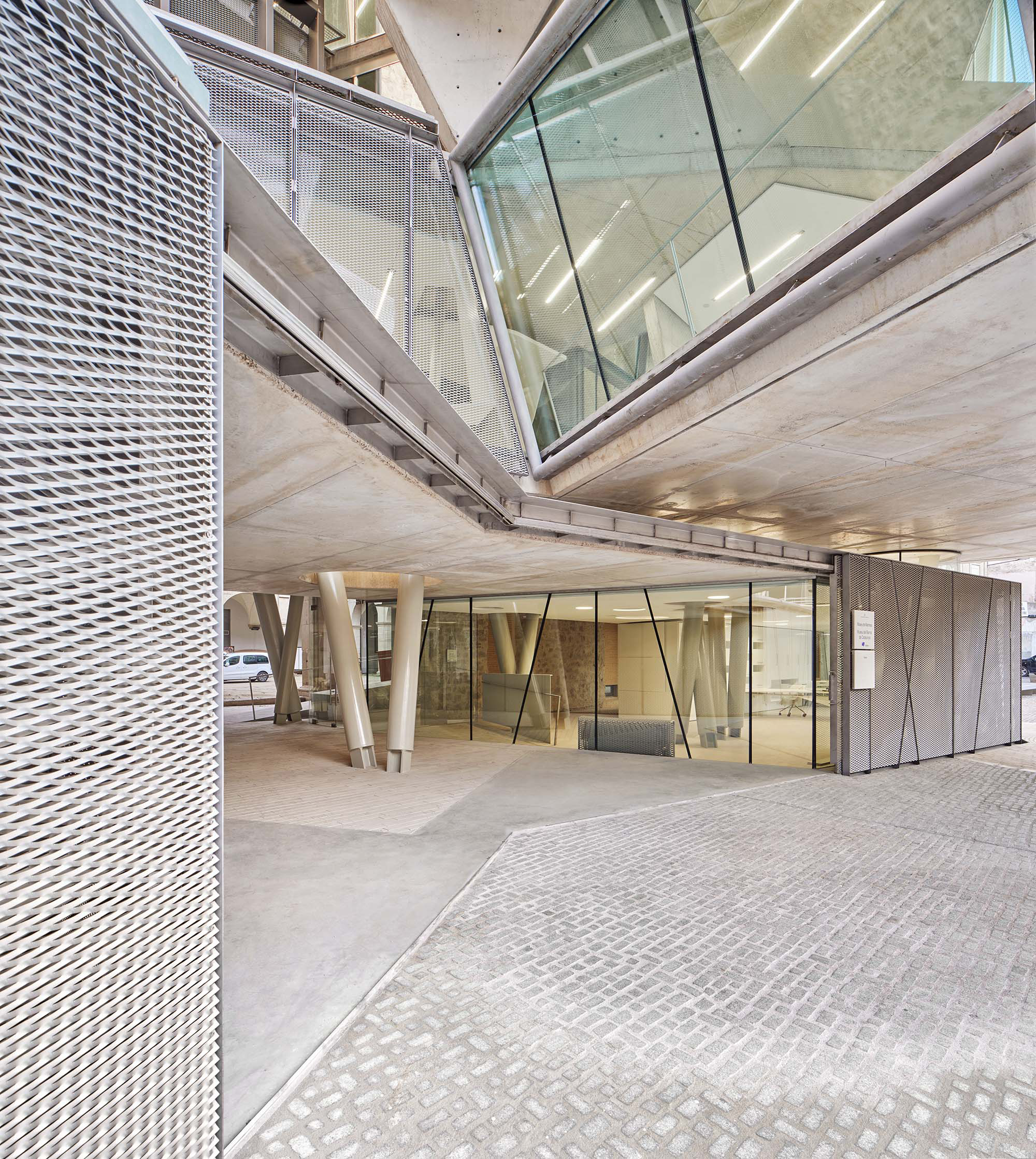
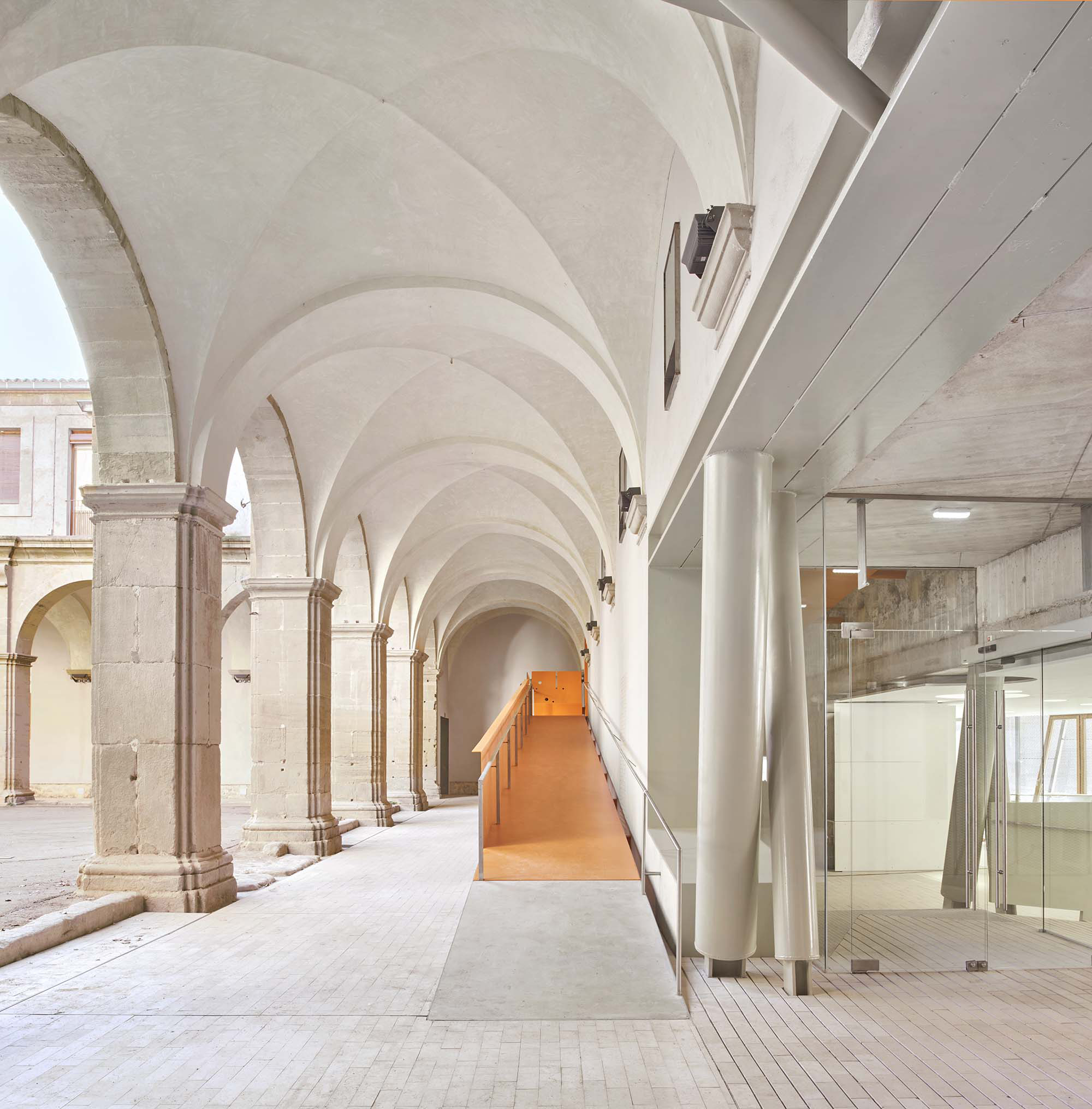
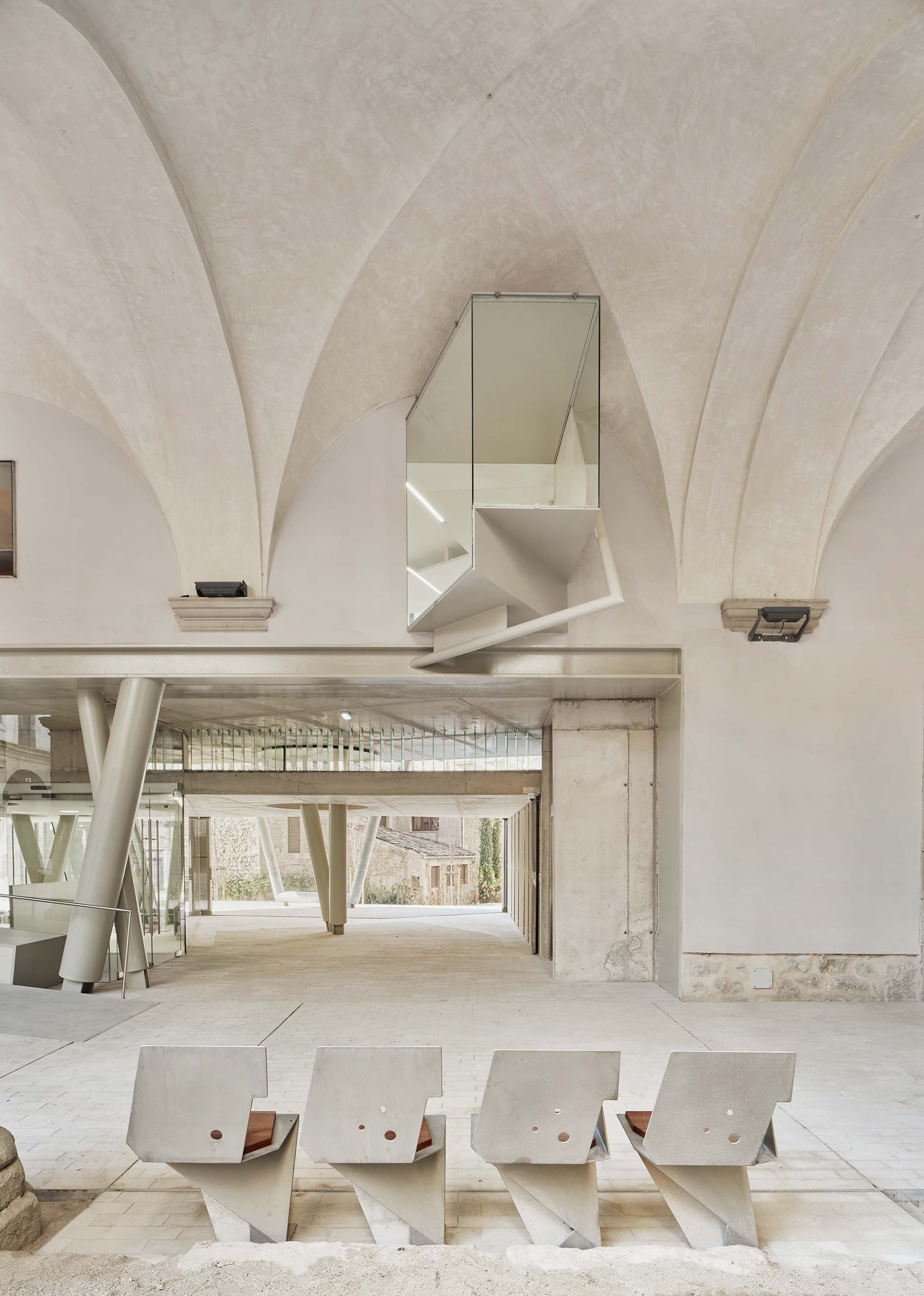
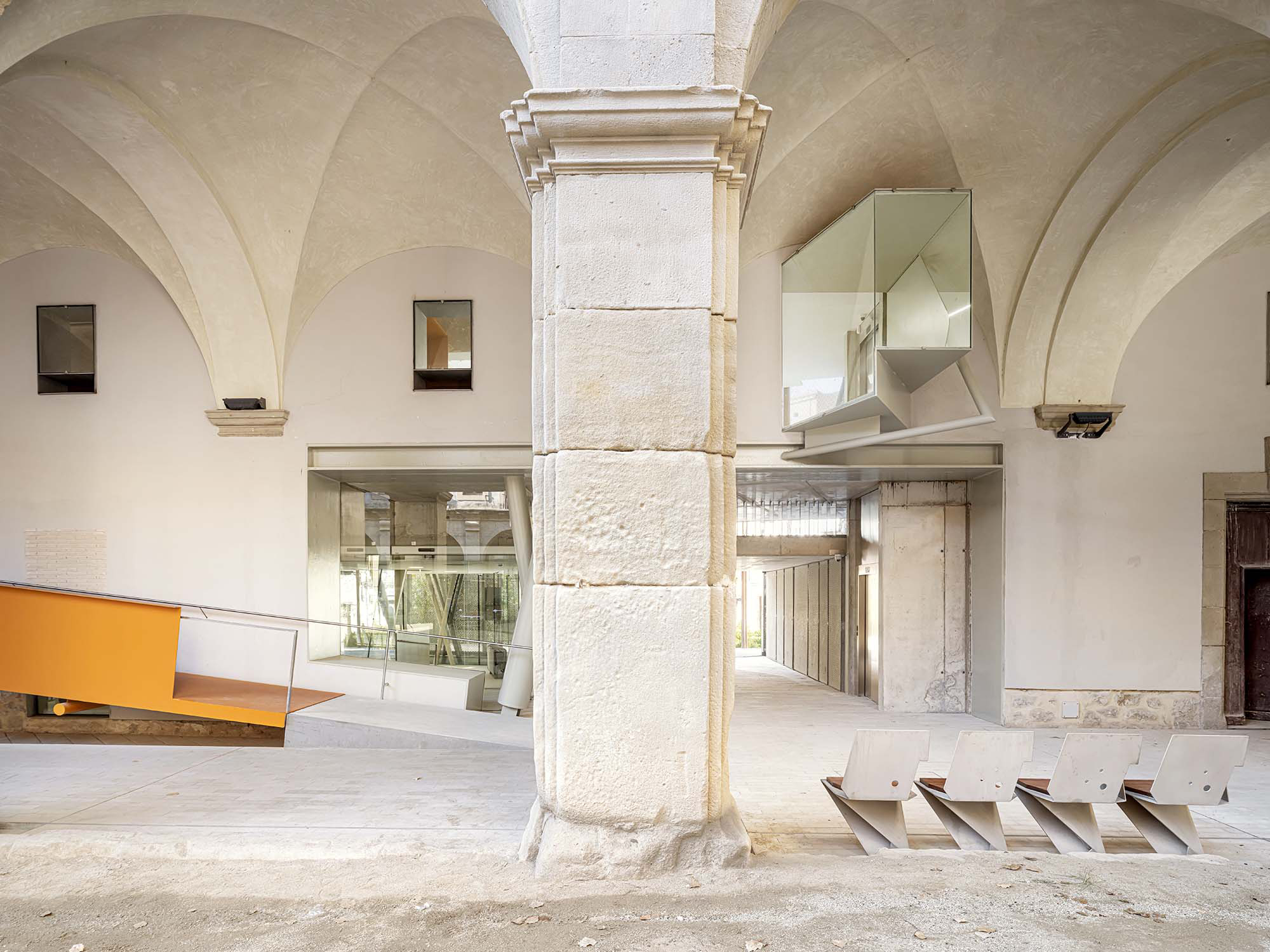
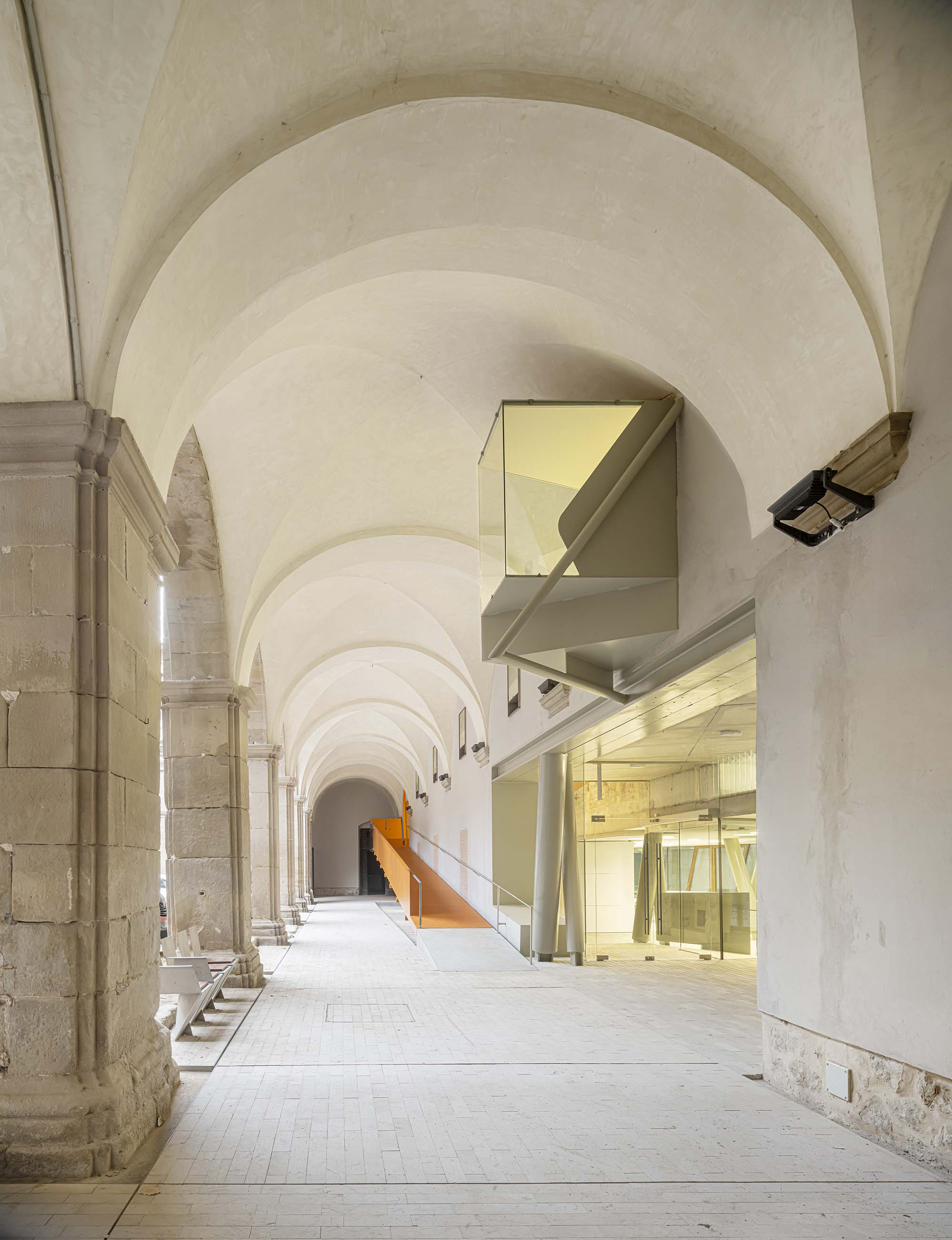
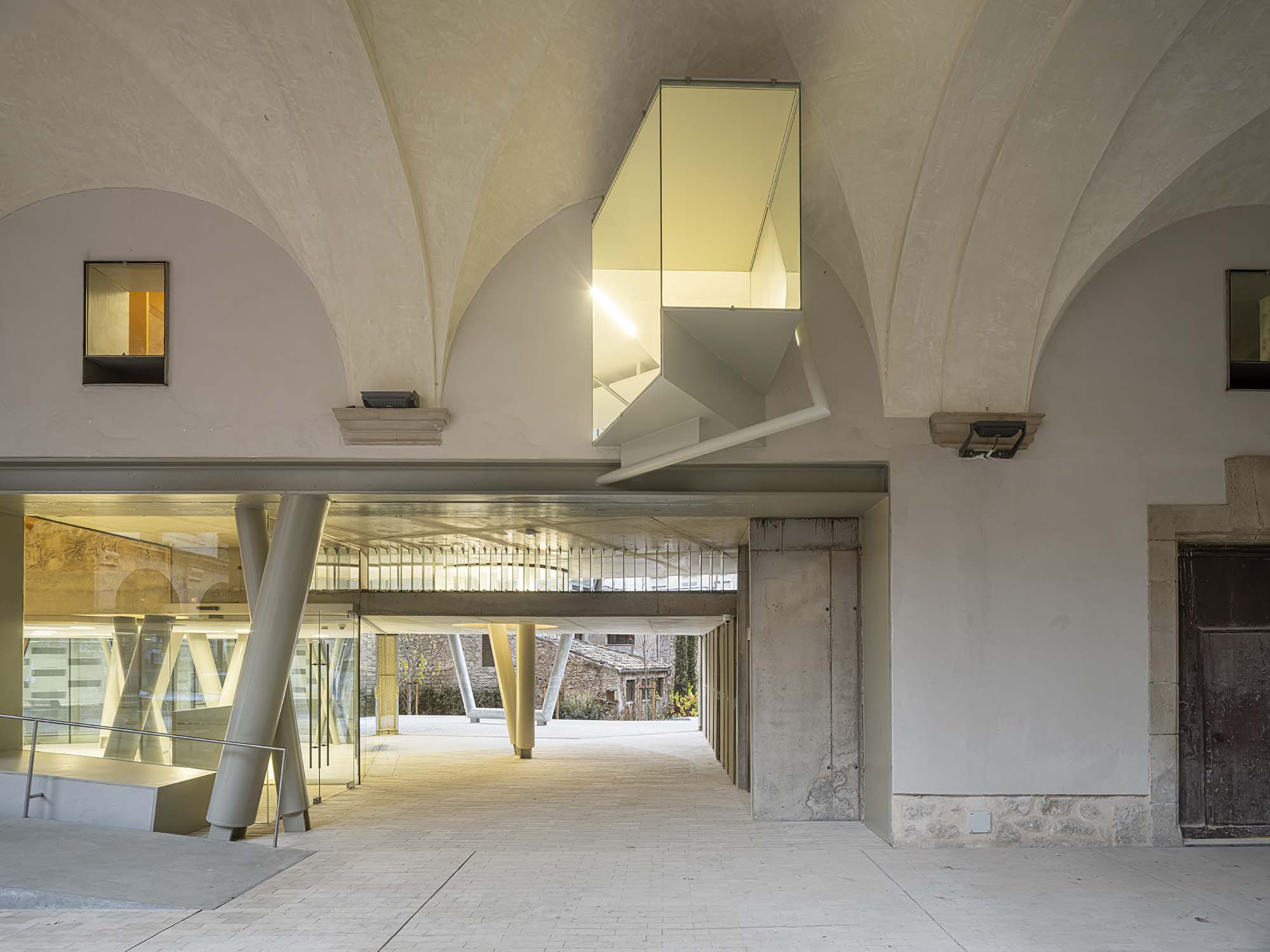
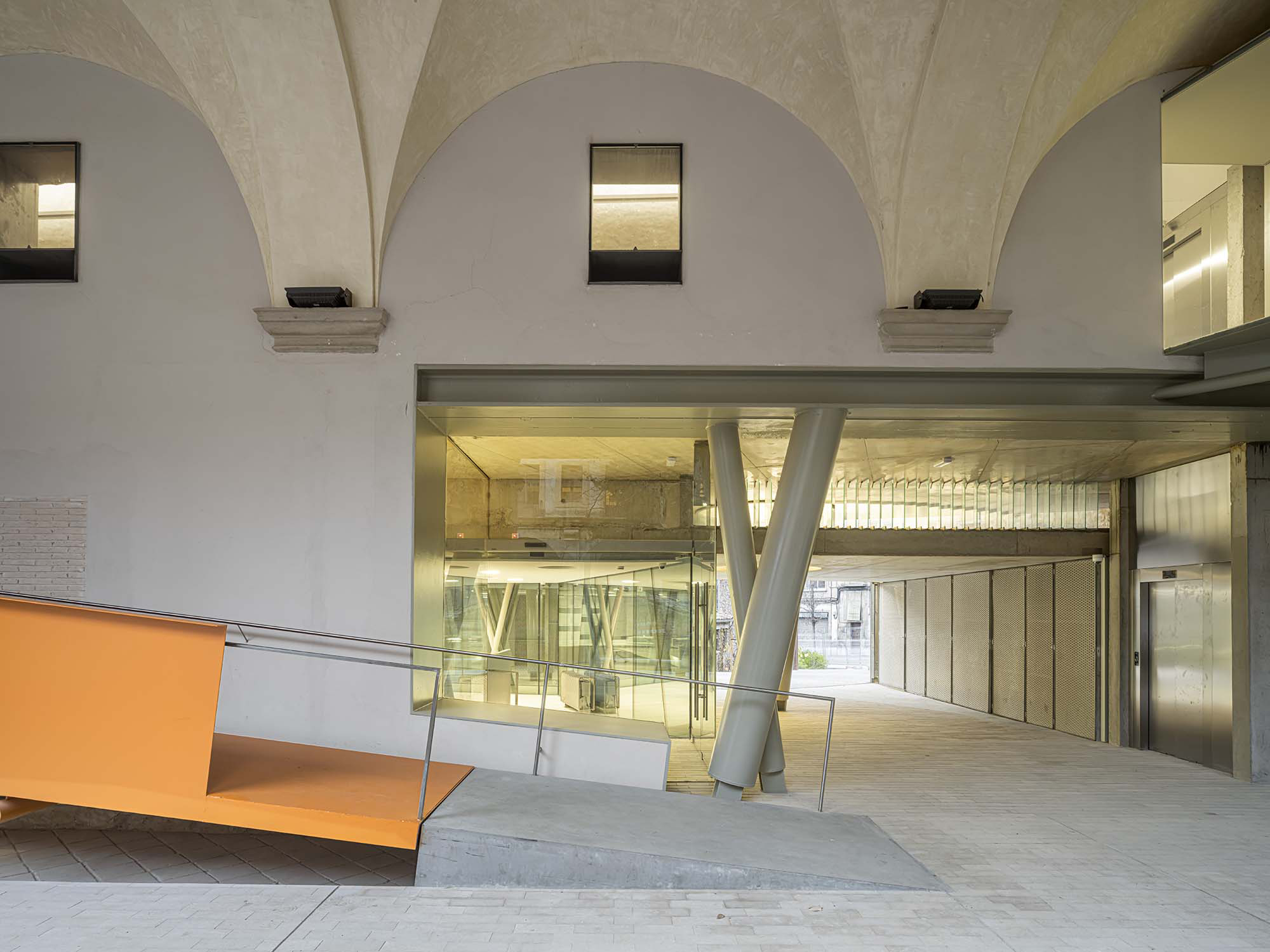
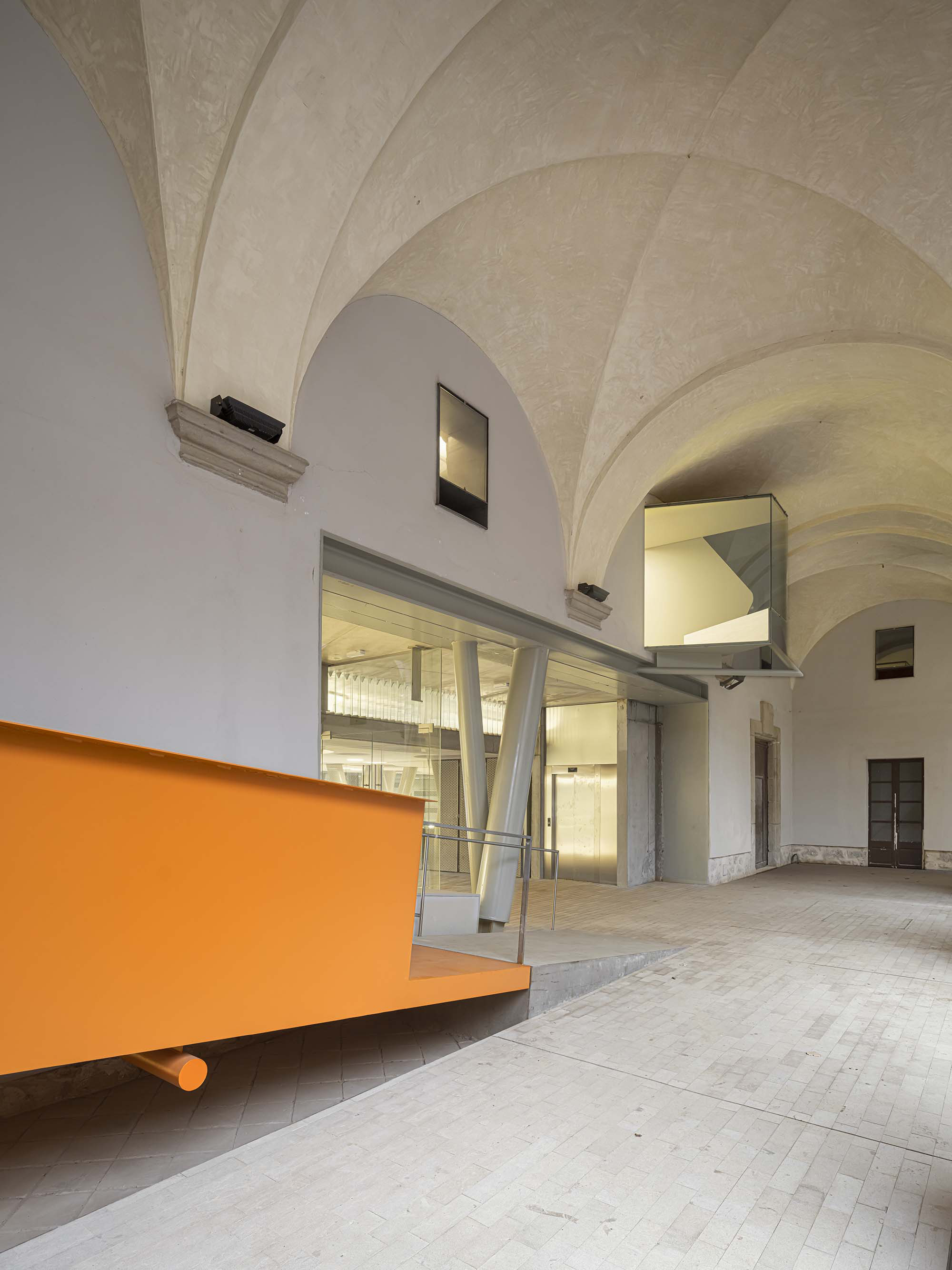
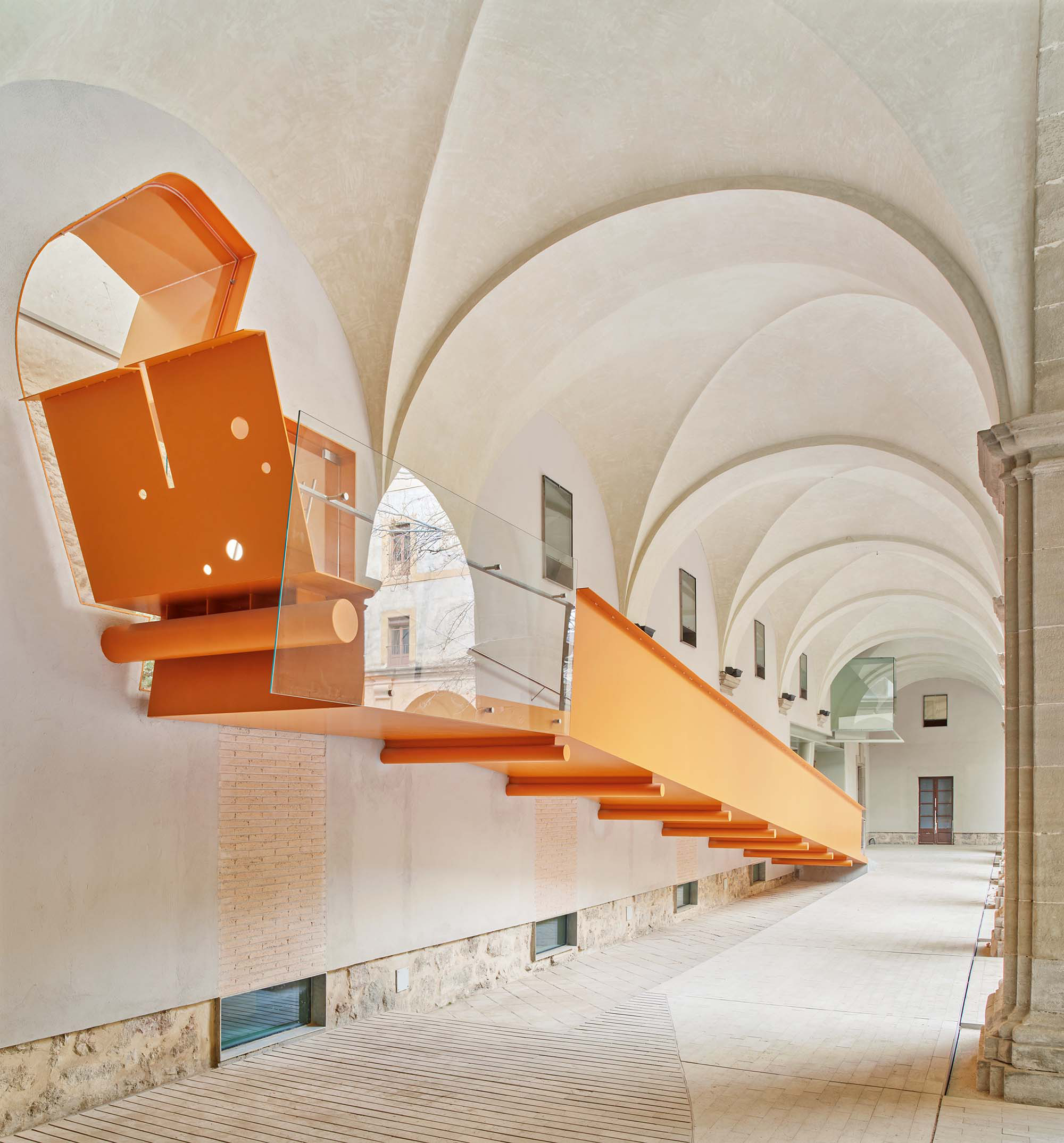
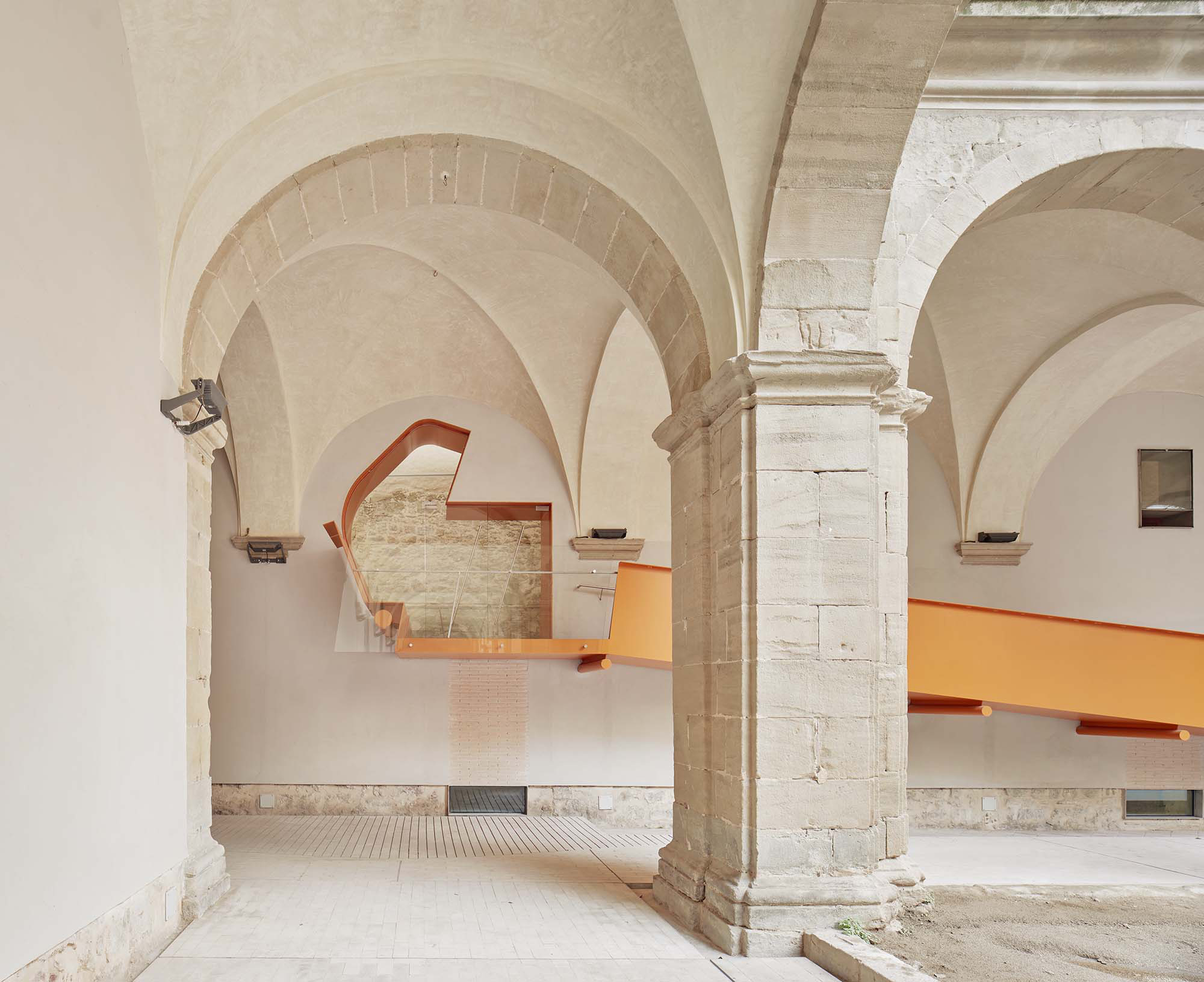
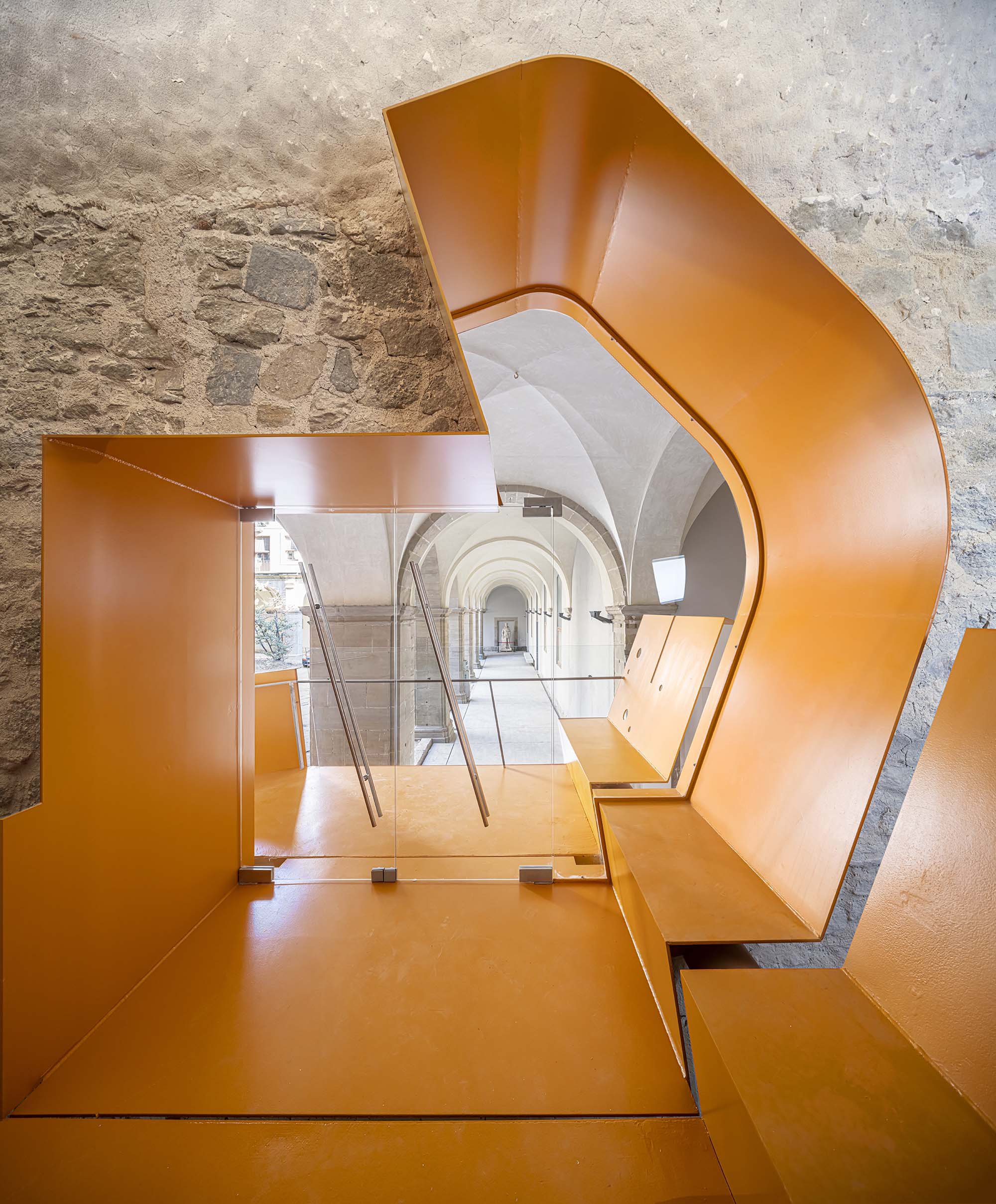
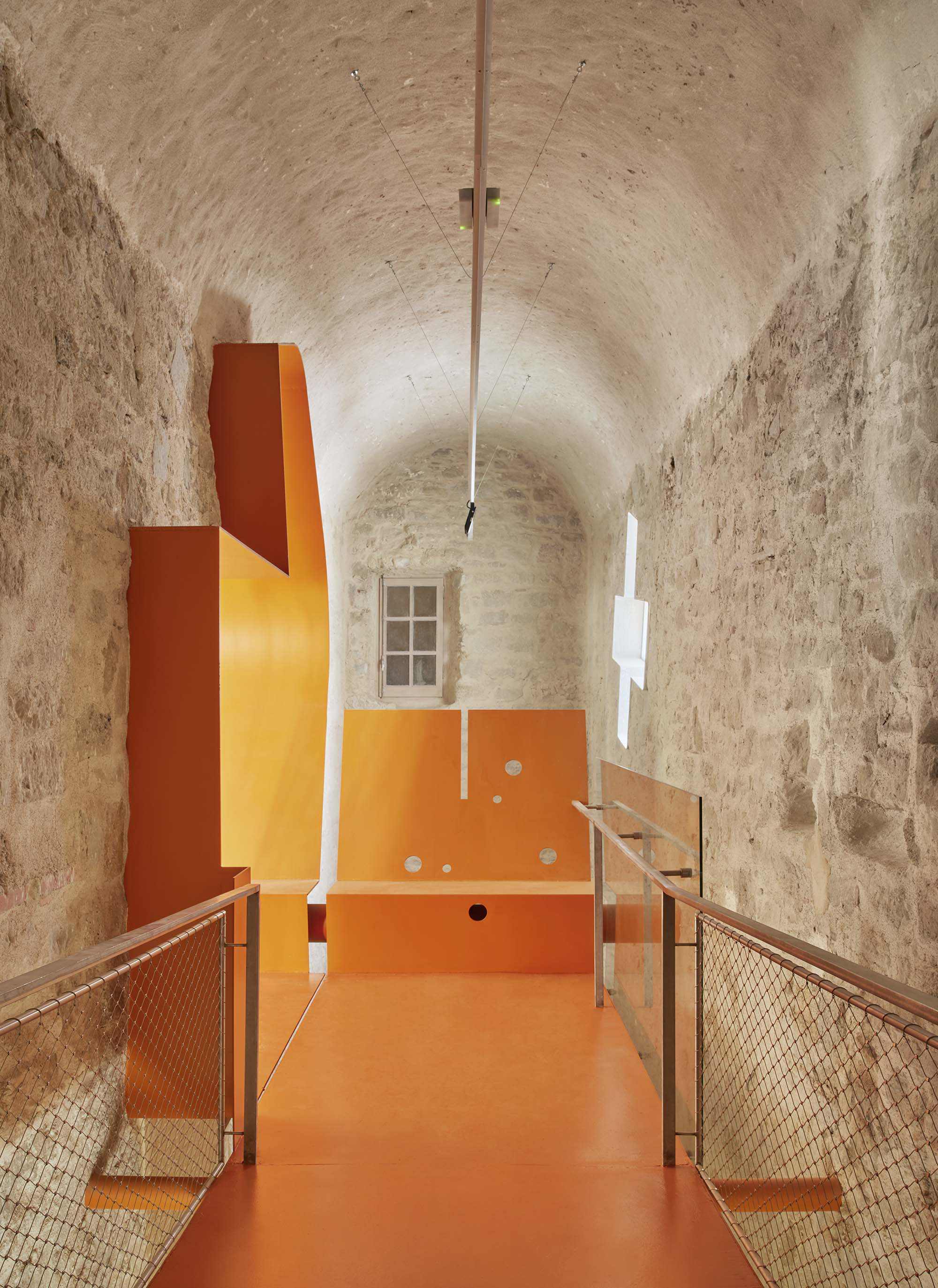
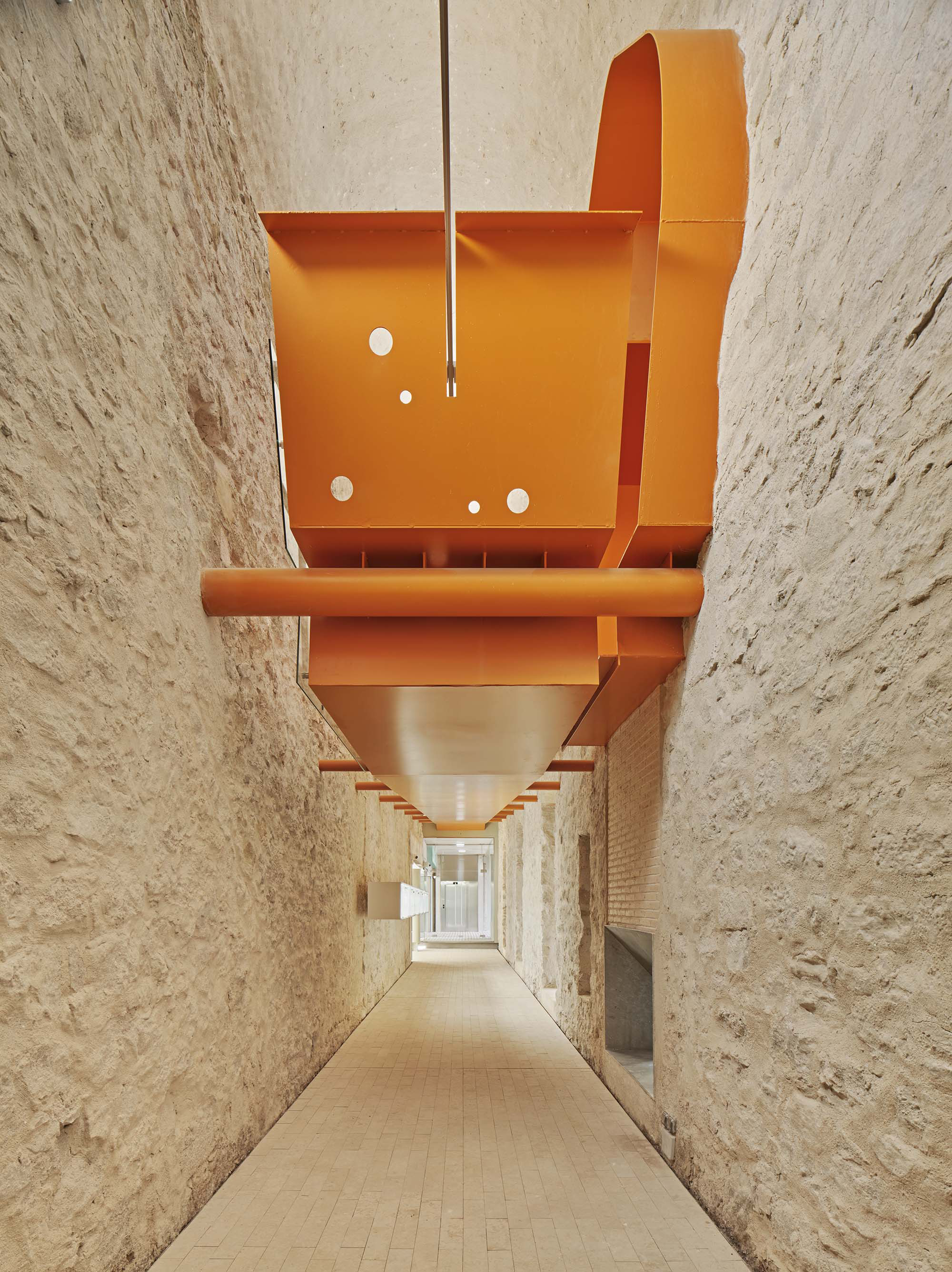
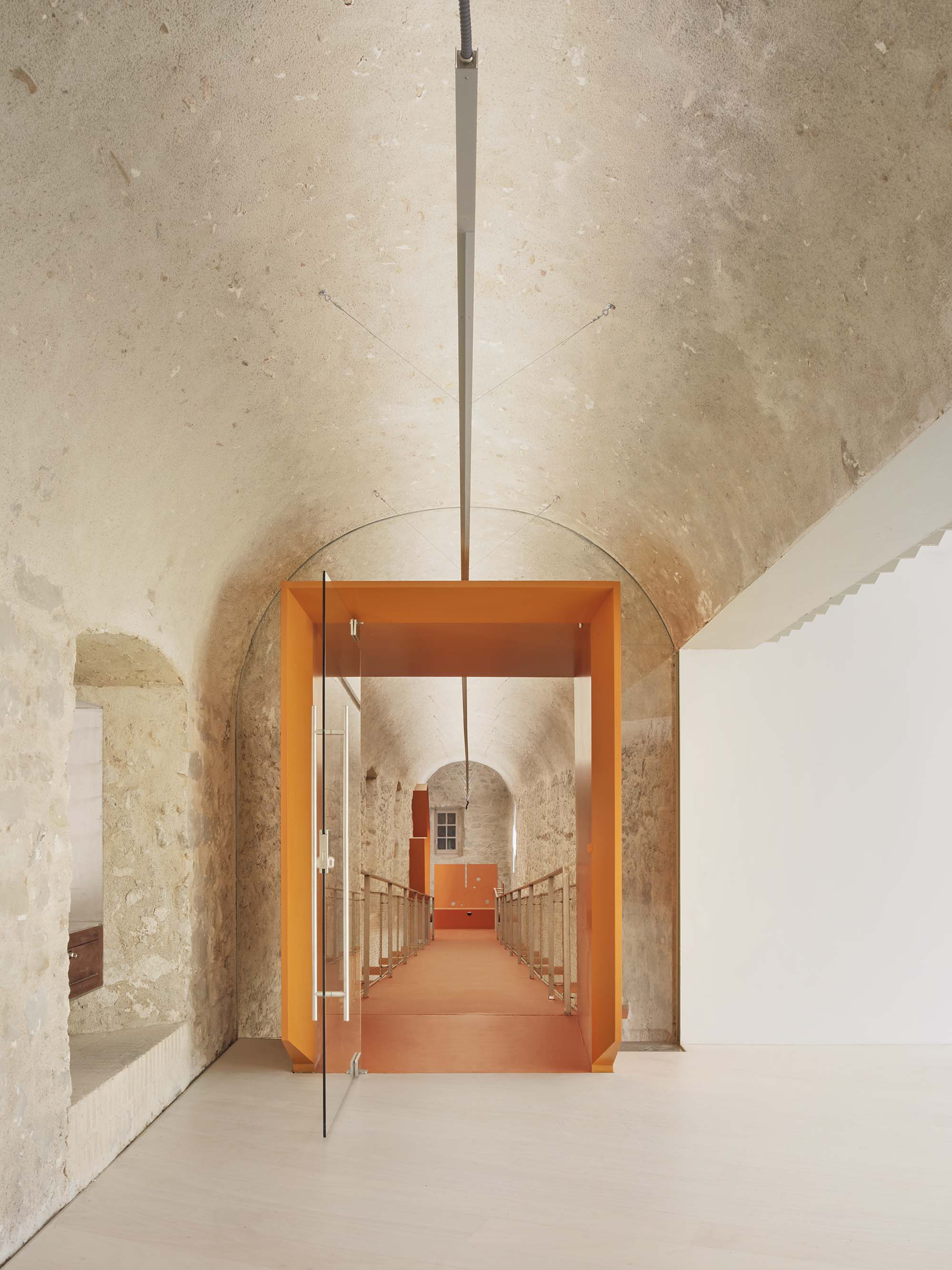
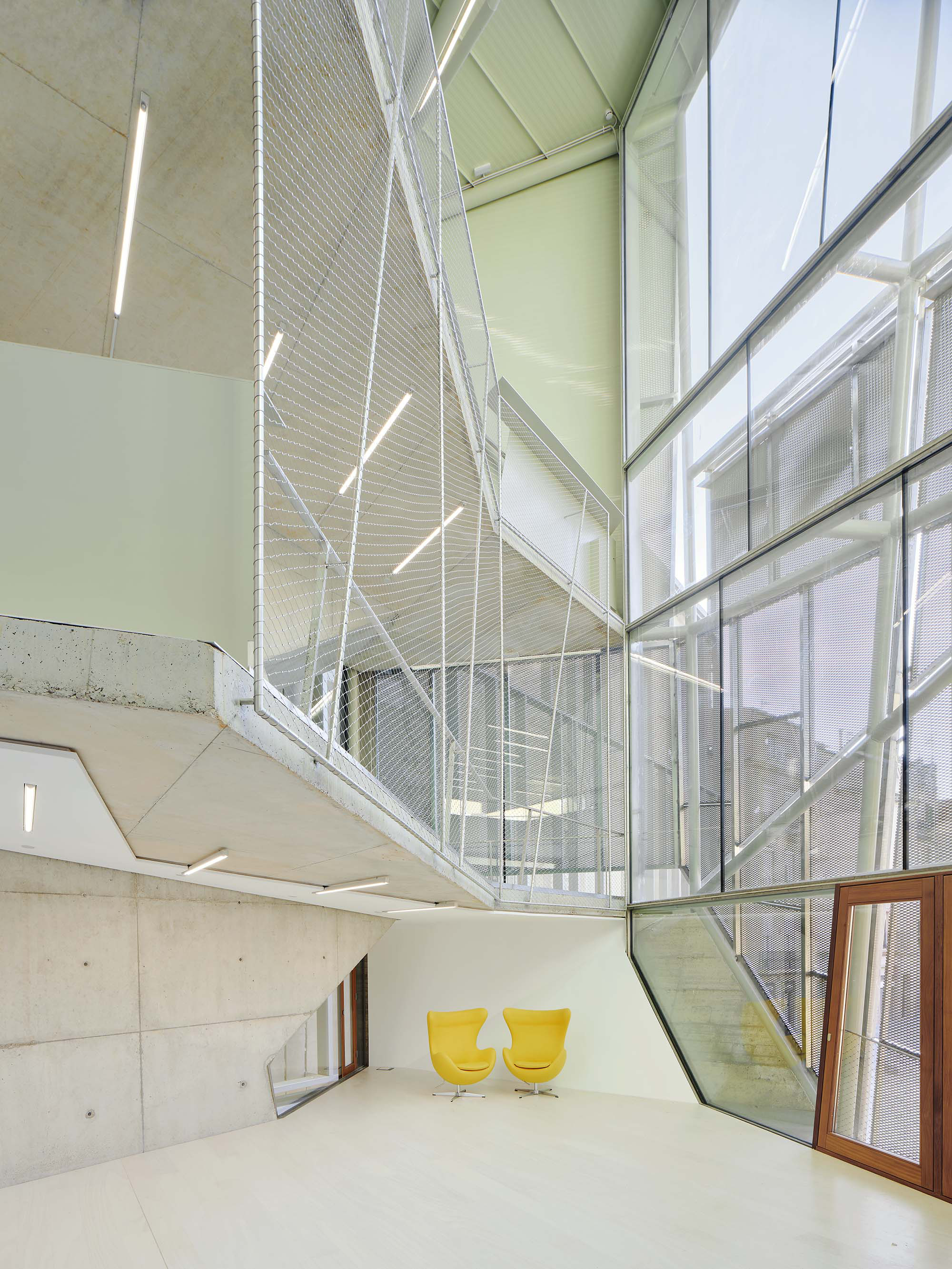
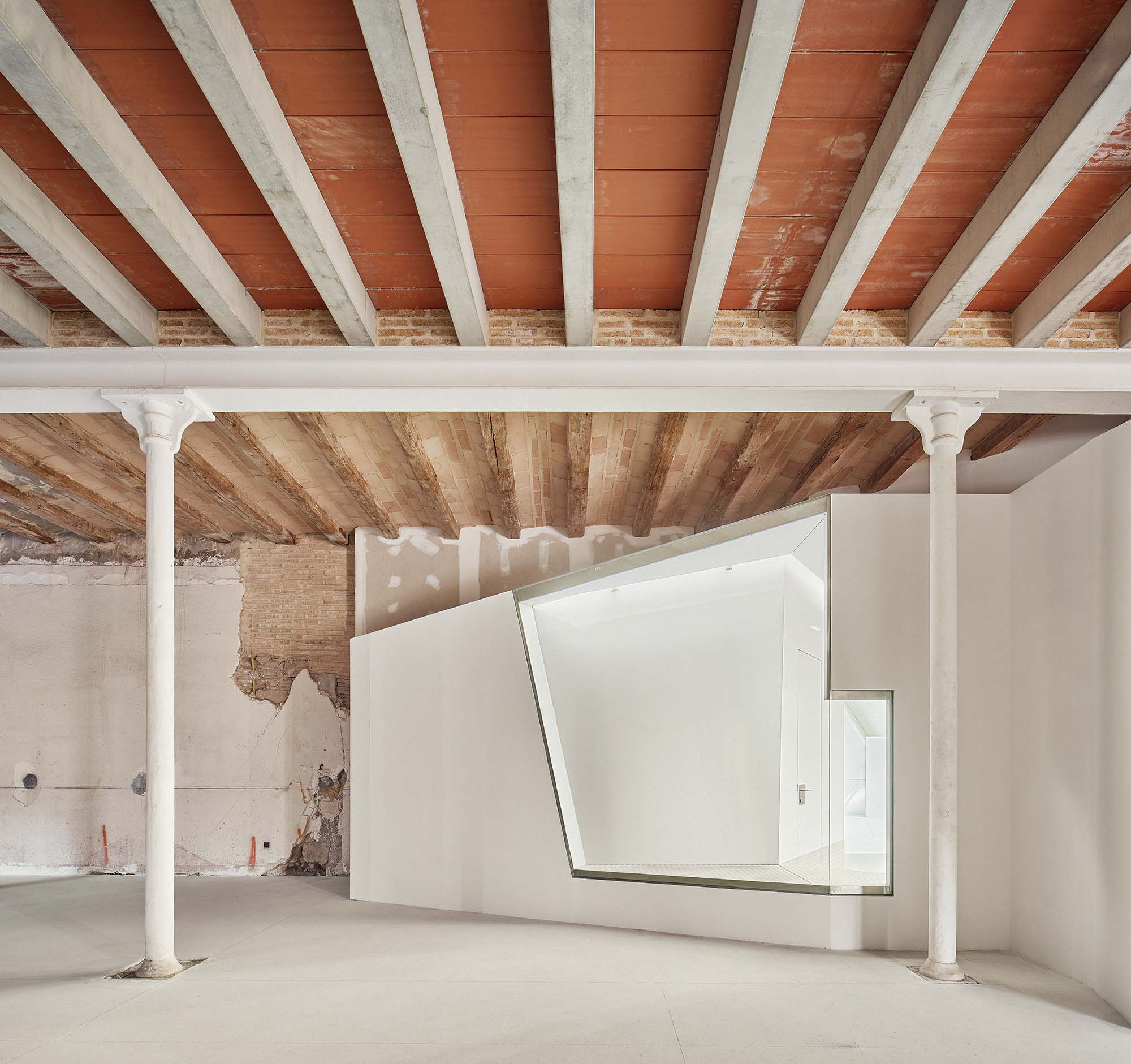
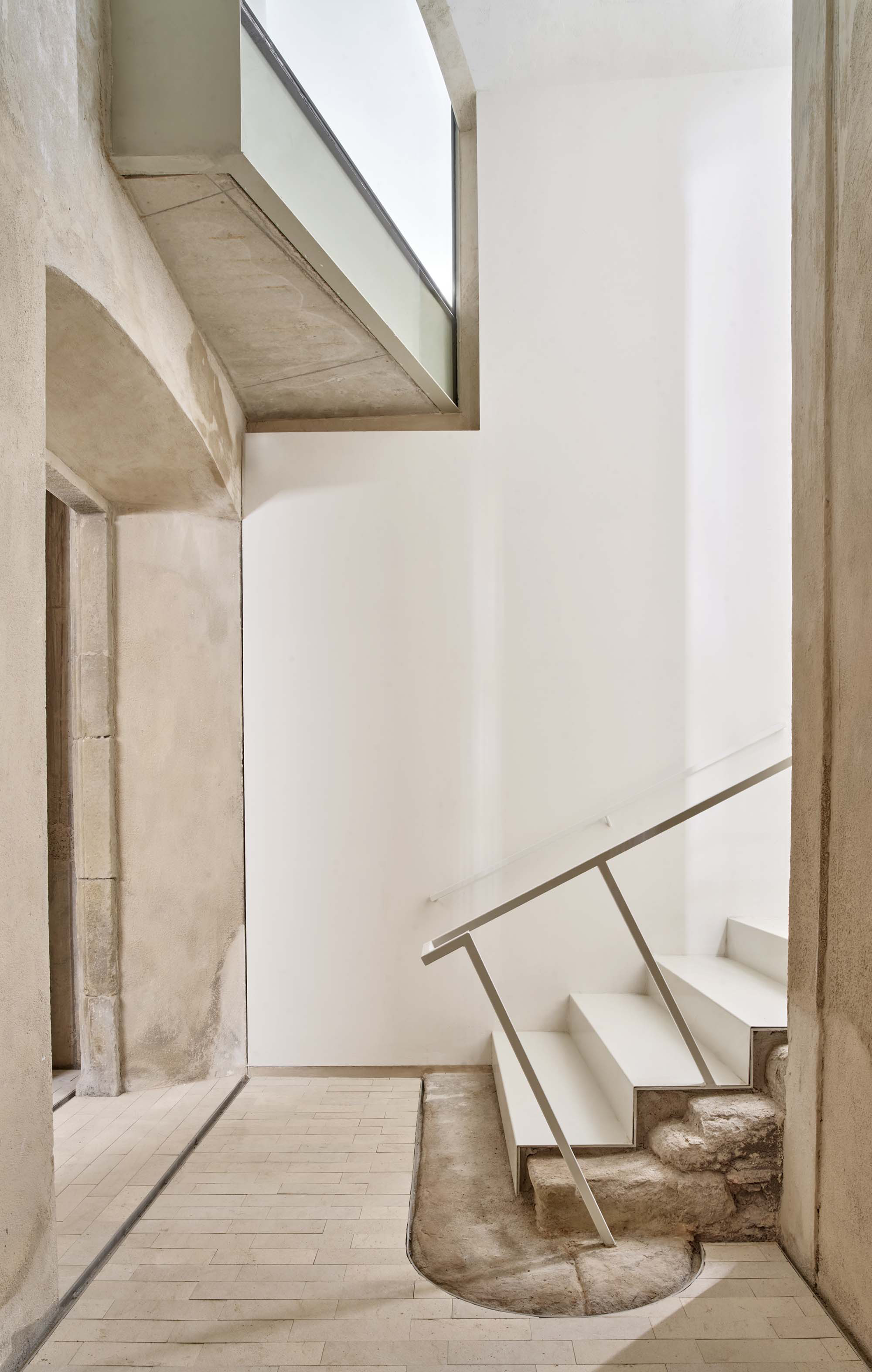
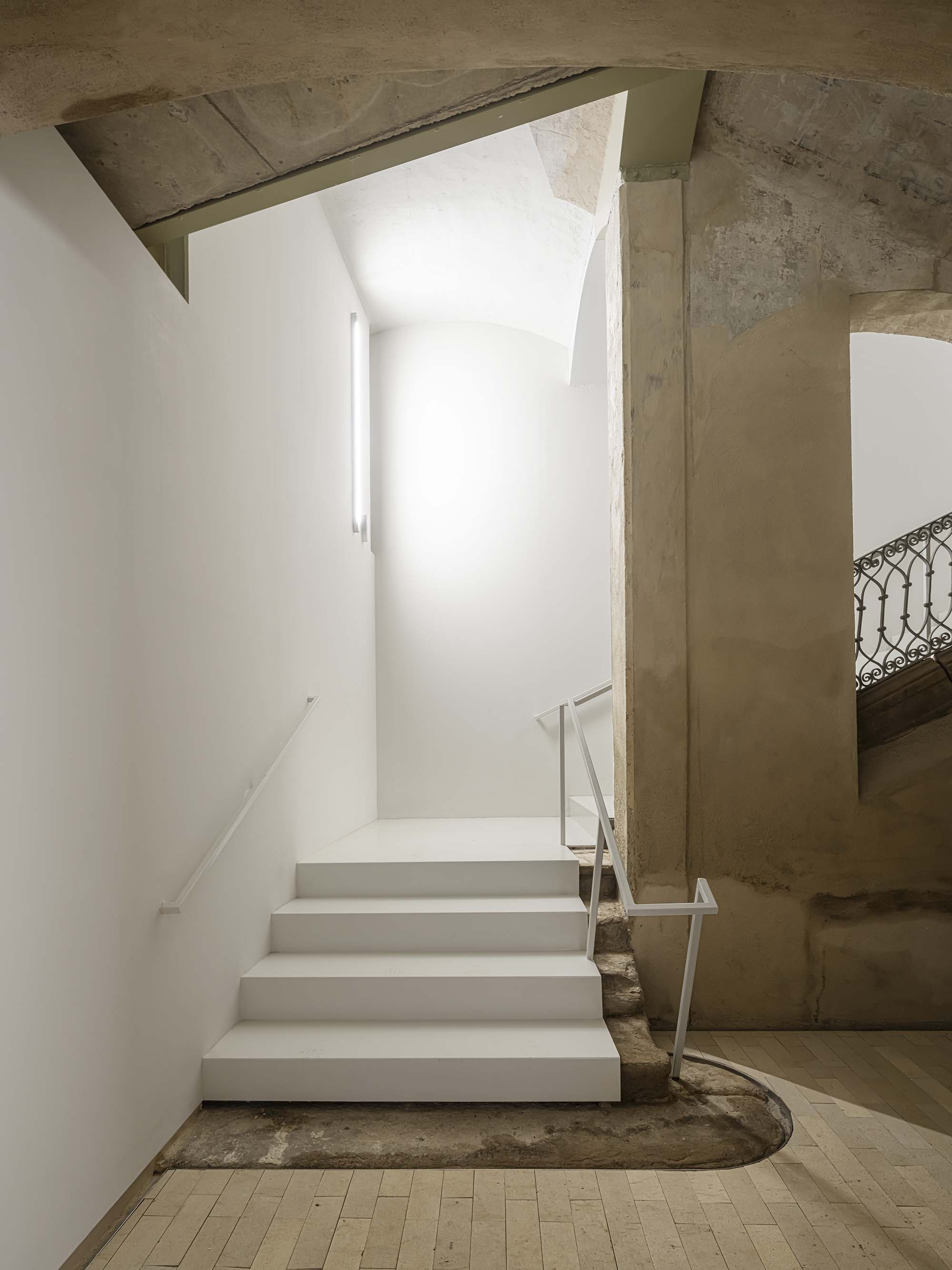
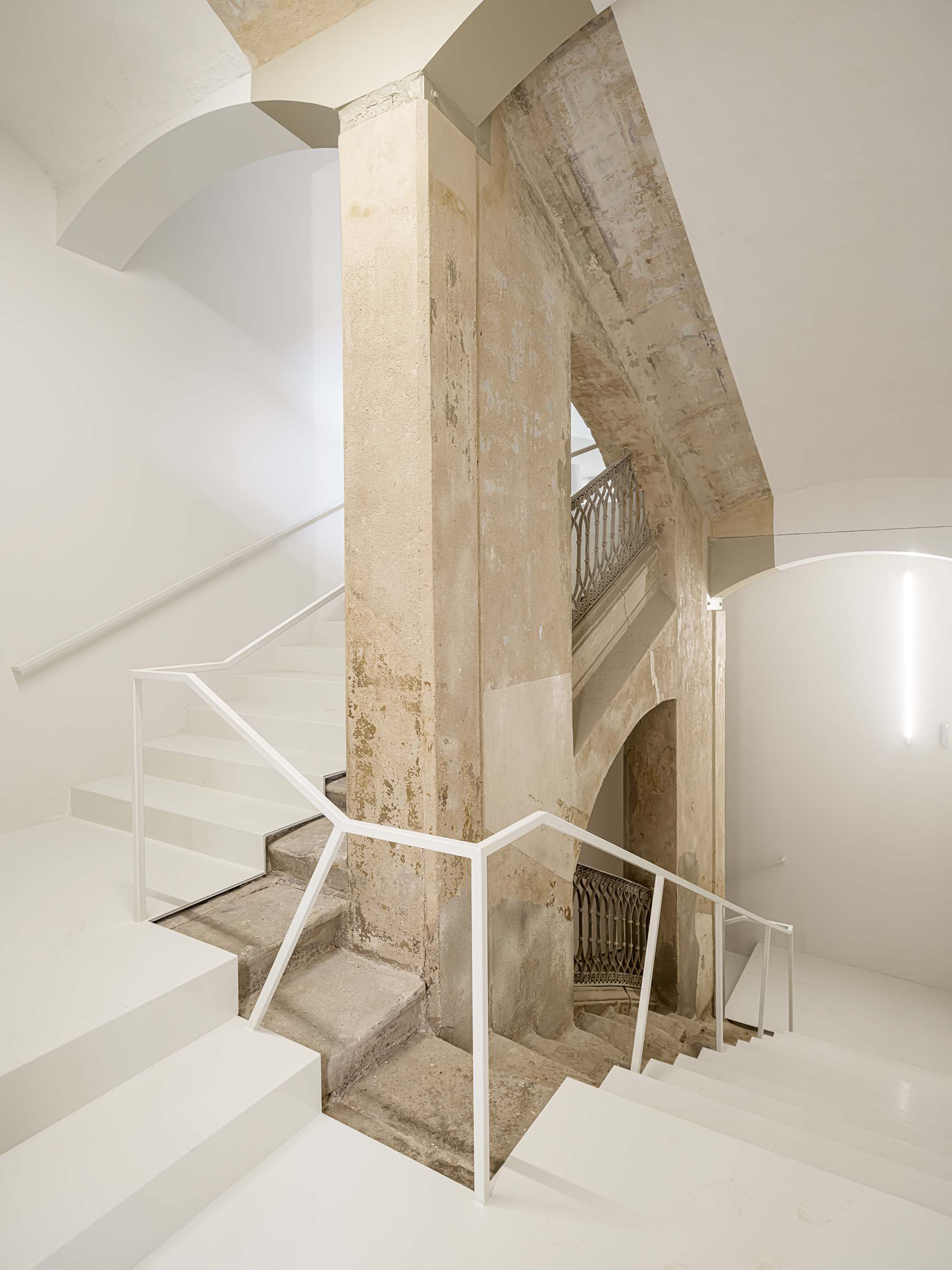
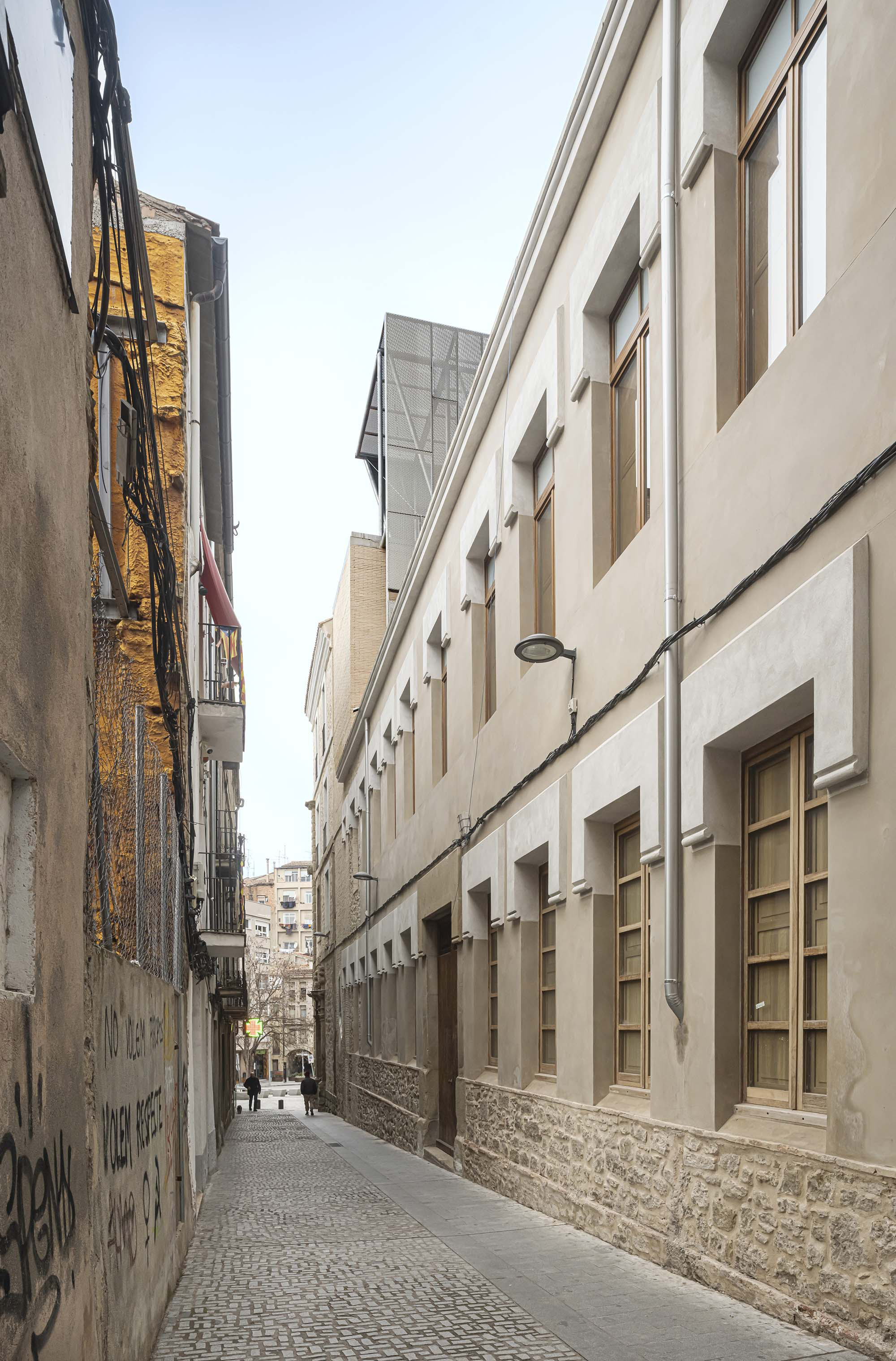
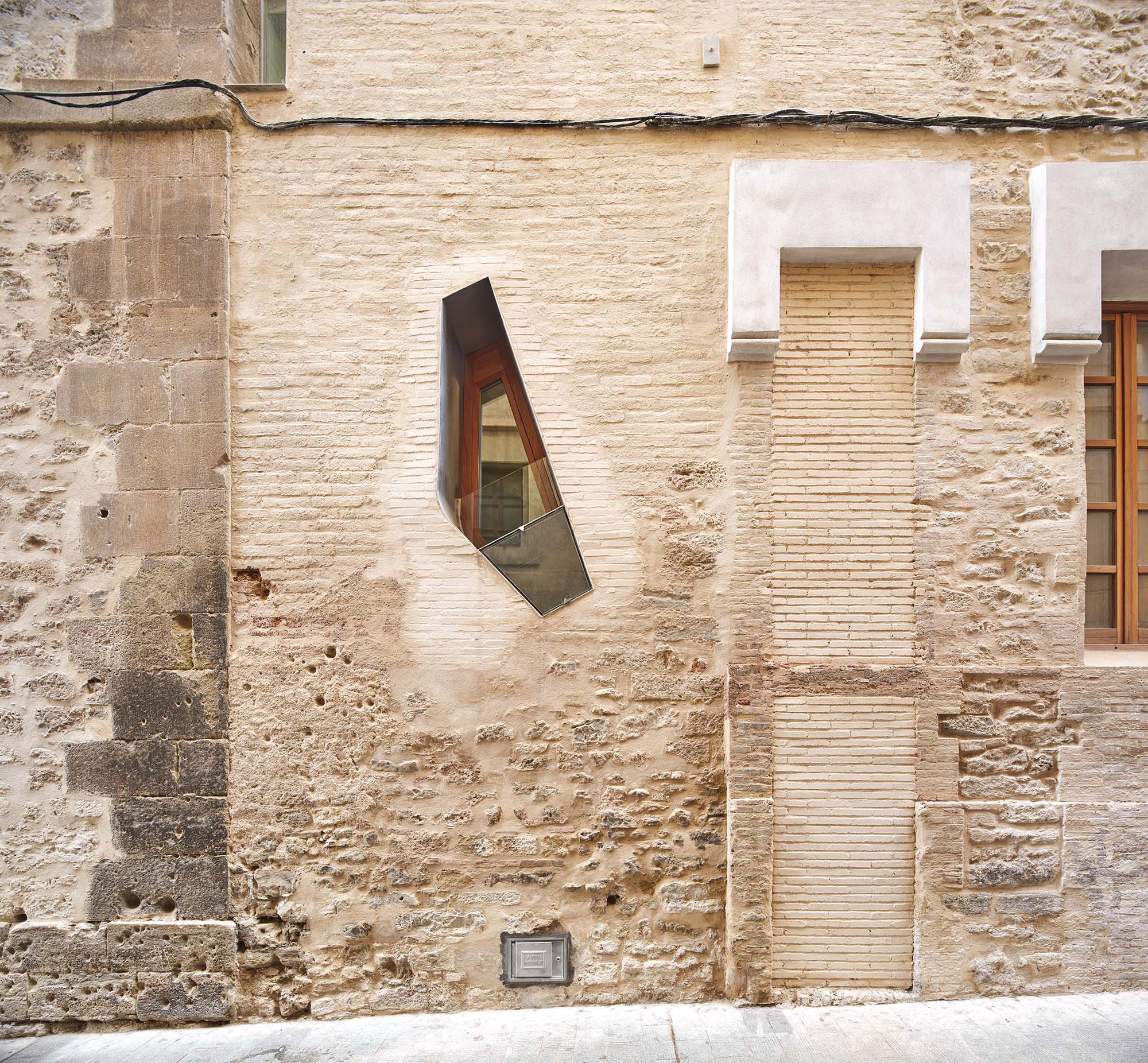
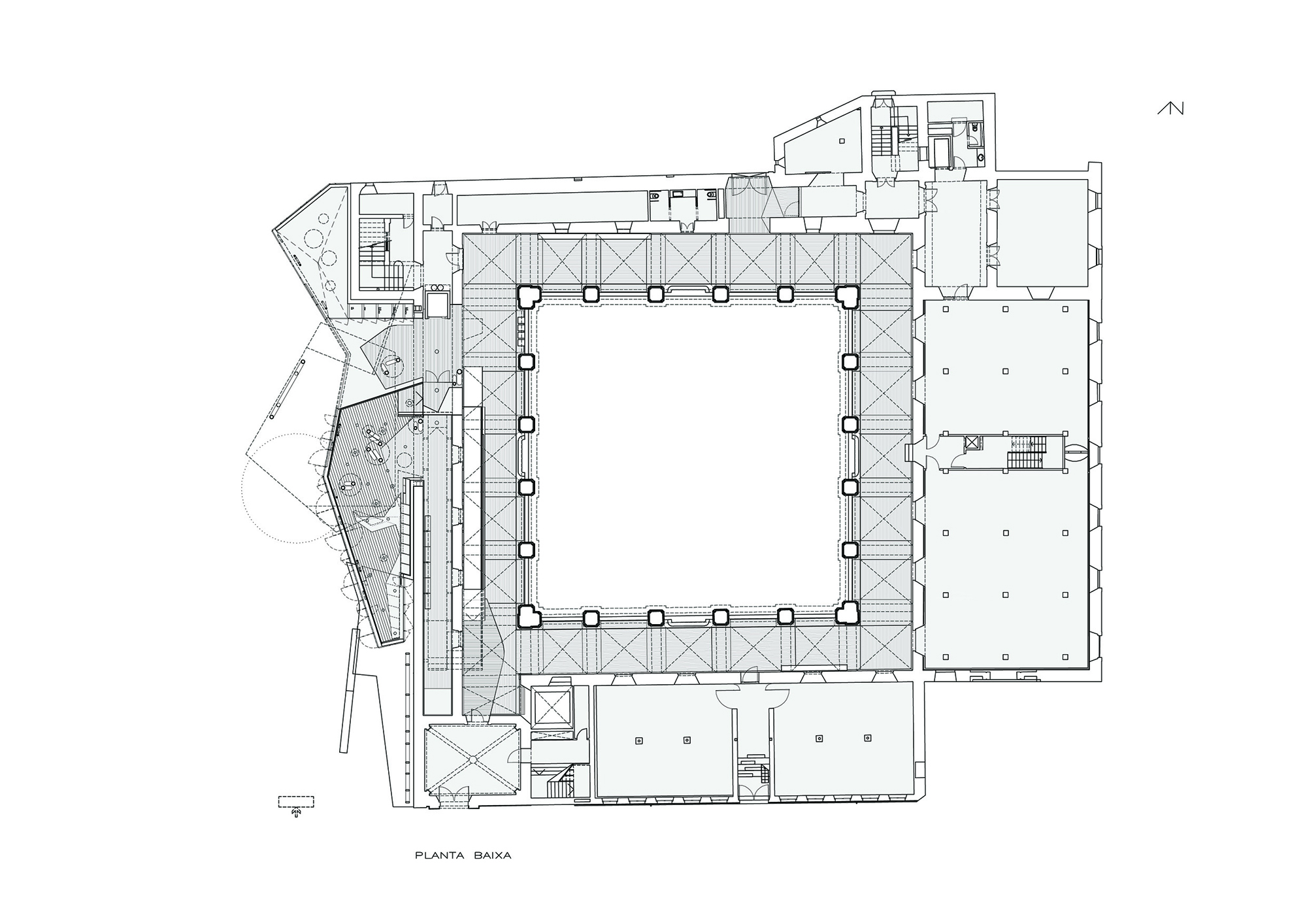
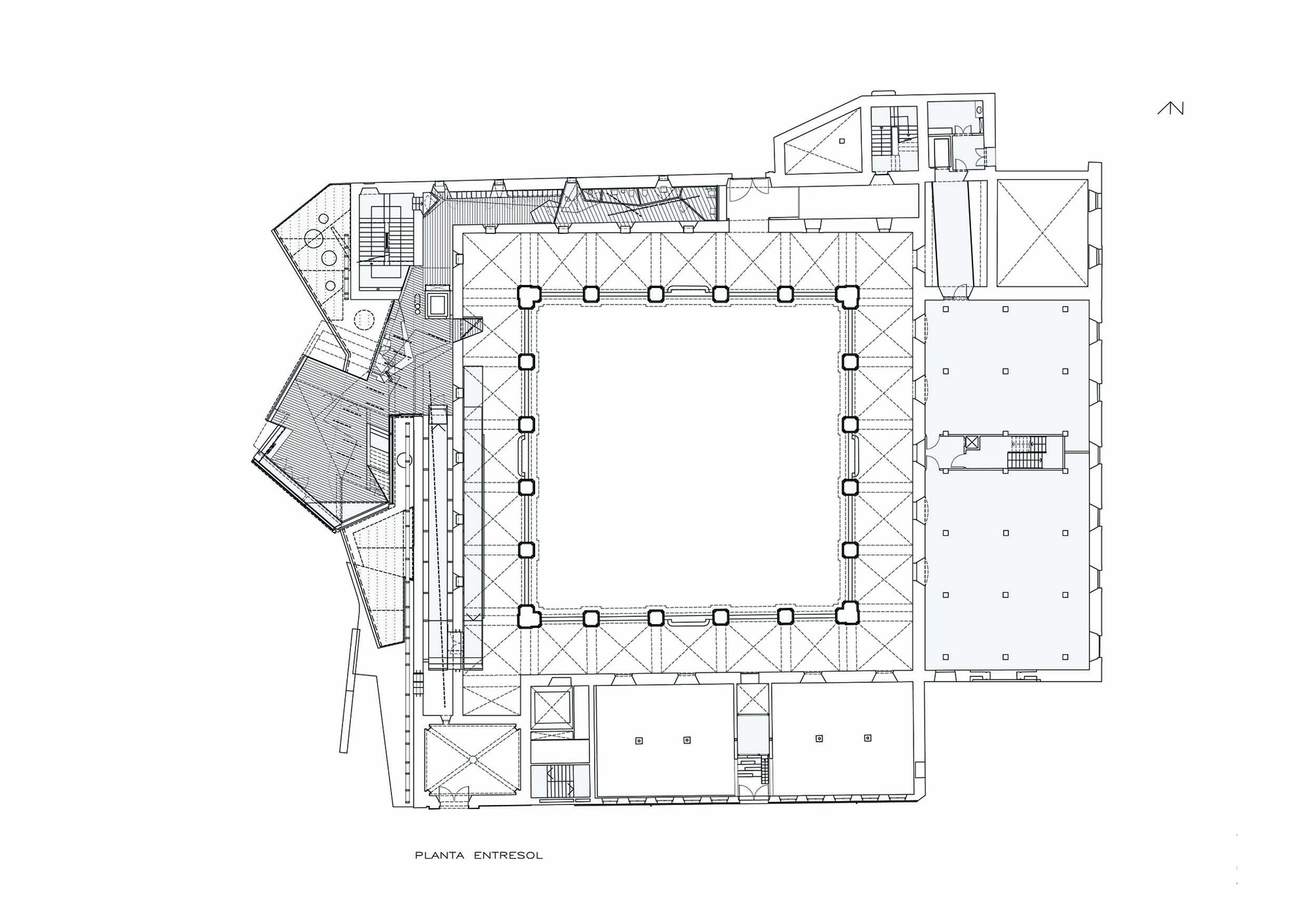
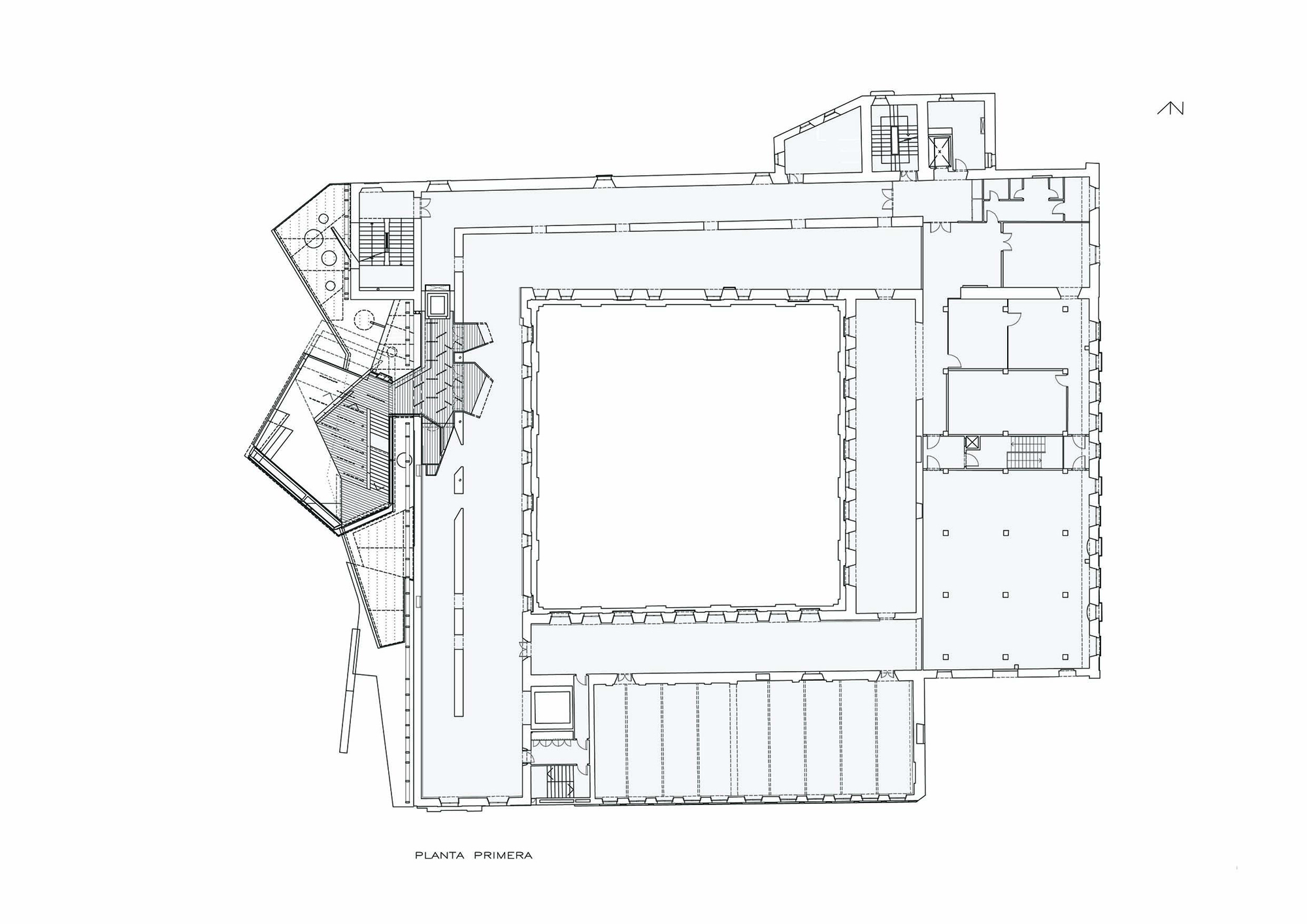
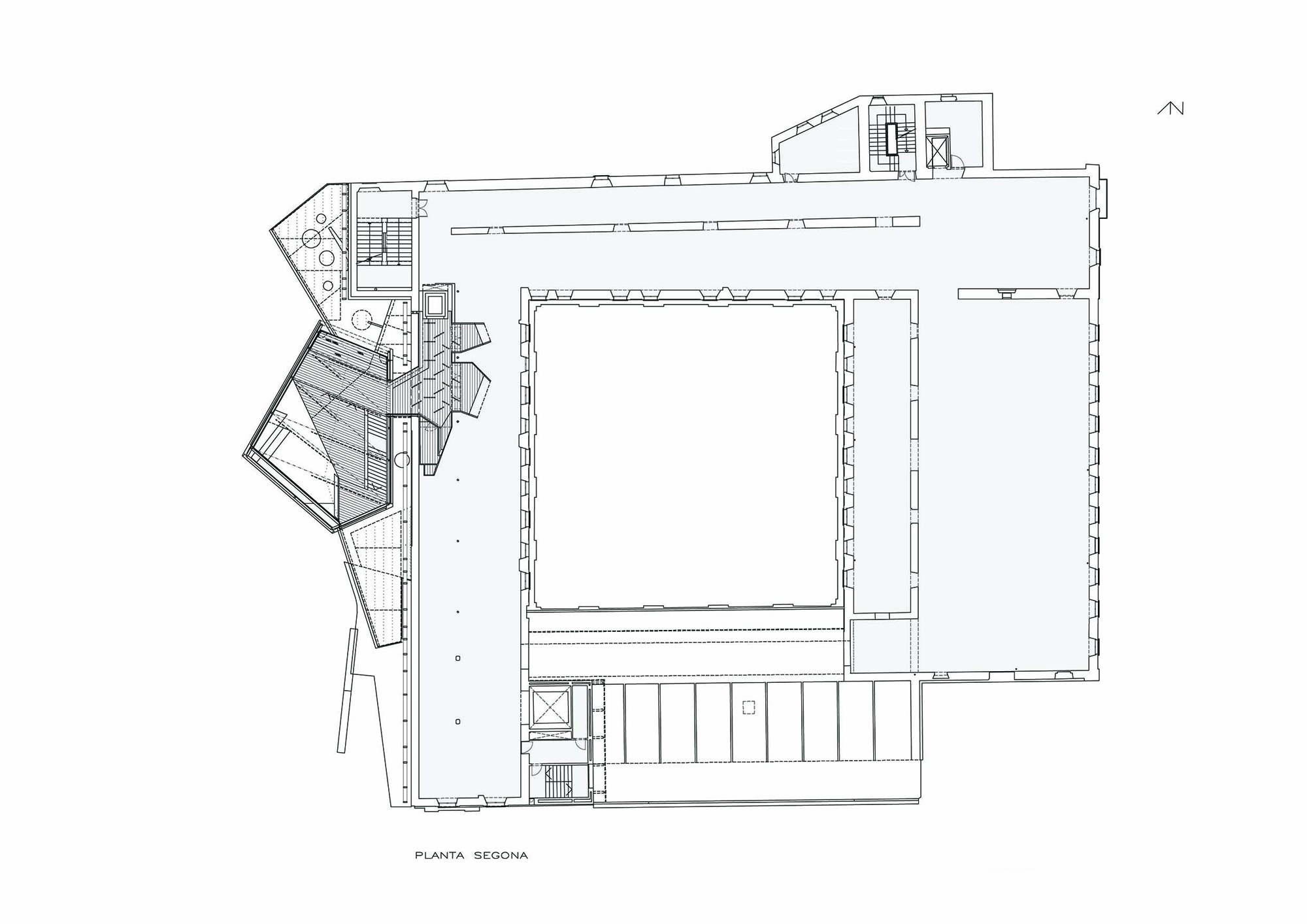
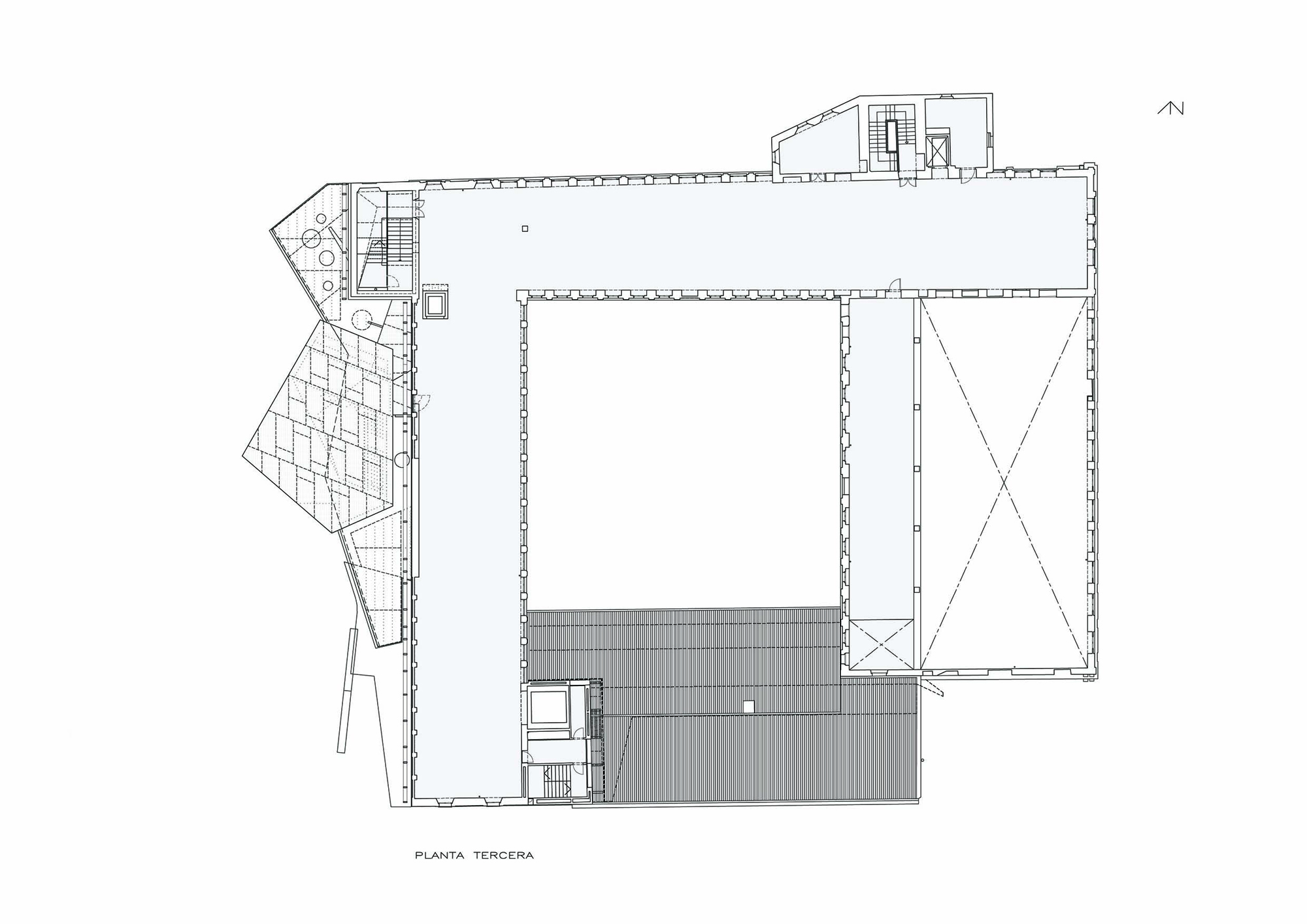
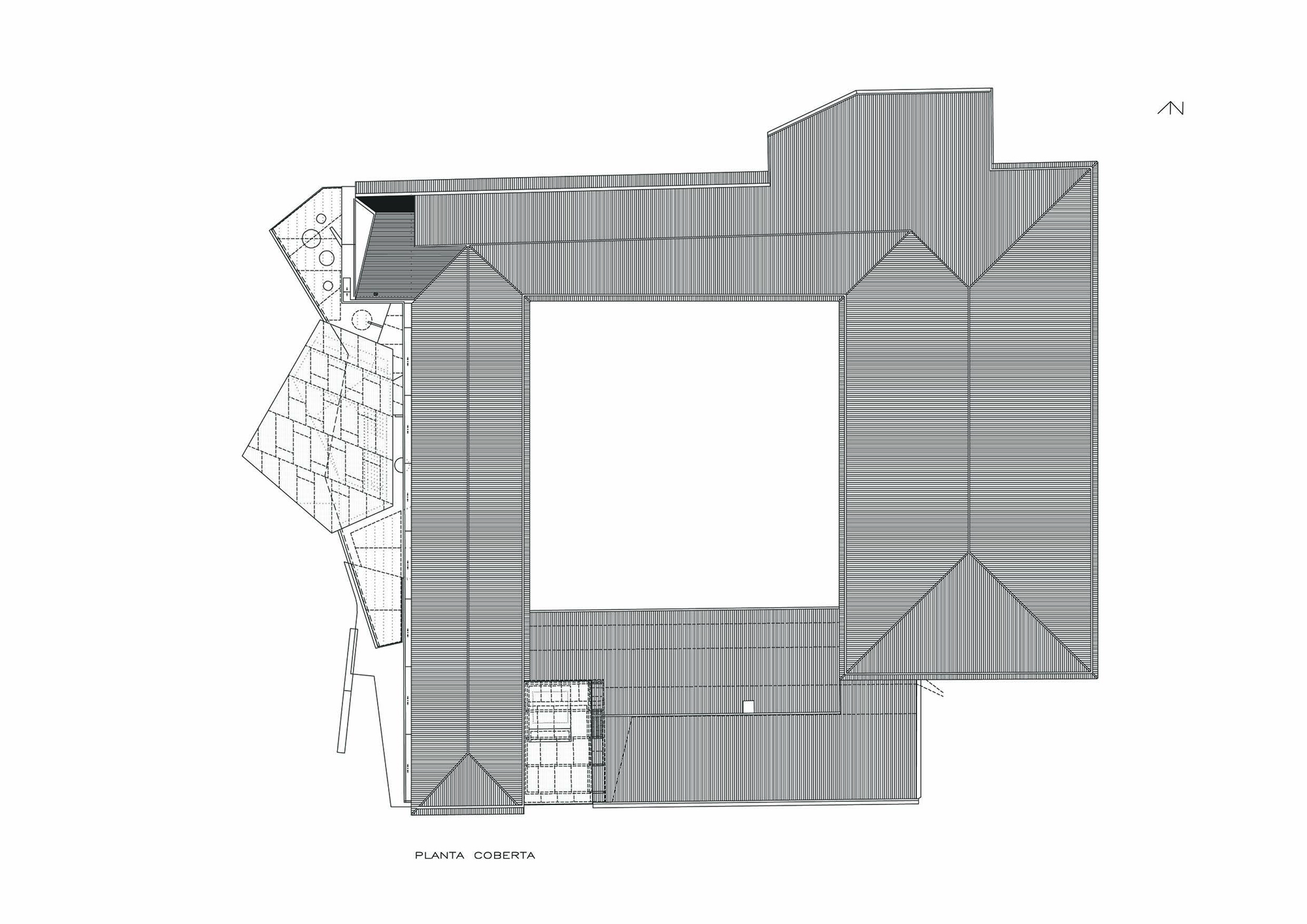
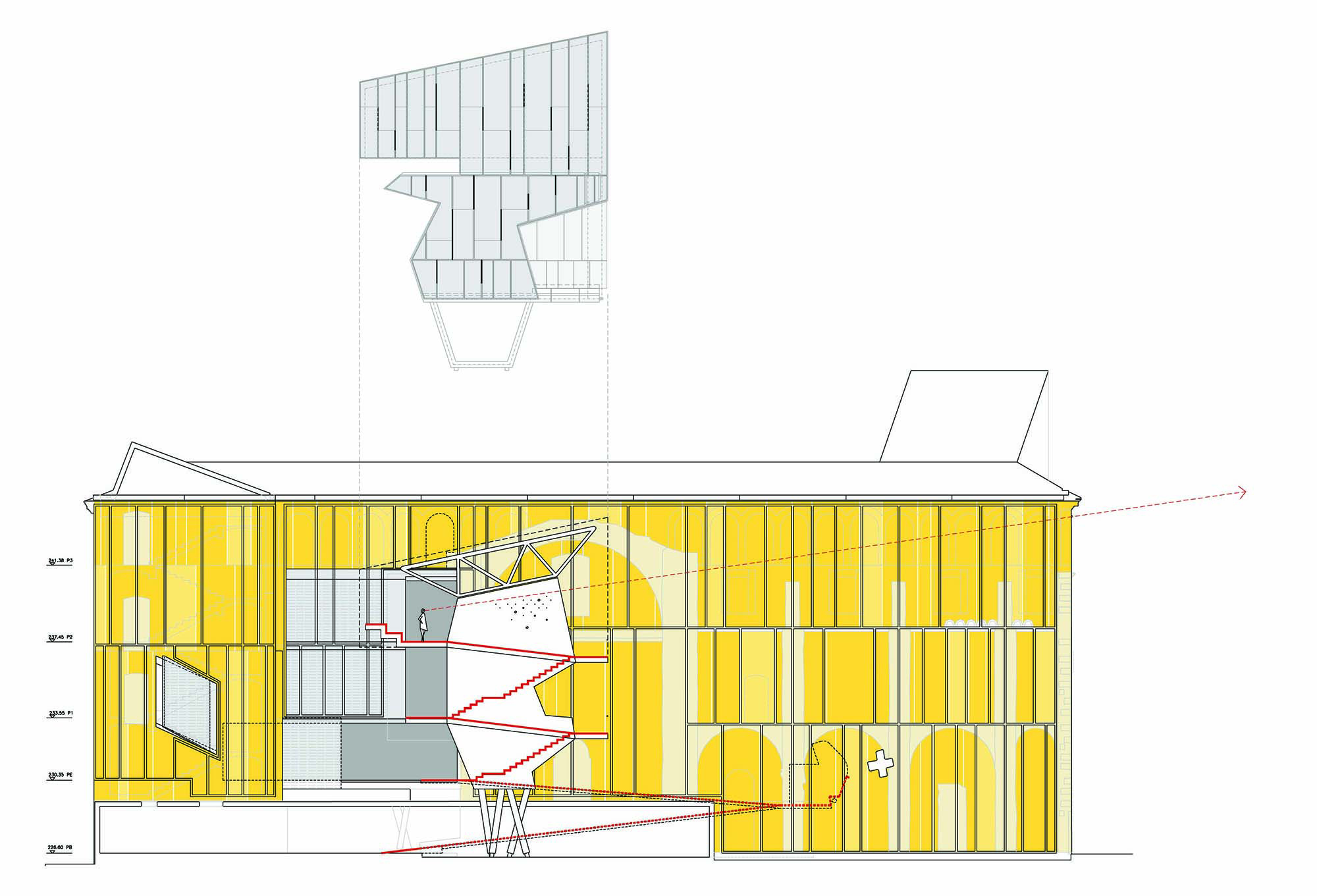
The project on the new accesses to the building proposes a set of volumes which include both the new spaces destined to the hall and the main new accesses to the exhibition floors of the museum. The new volumes, placed in front of the old partitioning wall of the church, are arranged in a way that allows the conformation of the new façade of the building but at the same time grant the sights to the most important footprints of the old church that remains on the partitioning wall.
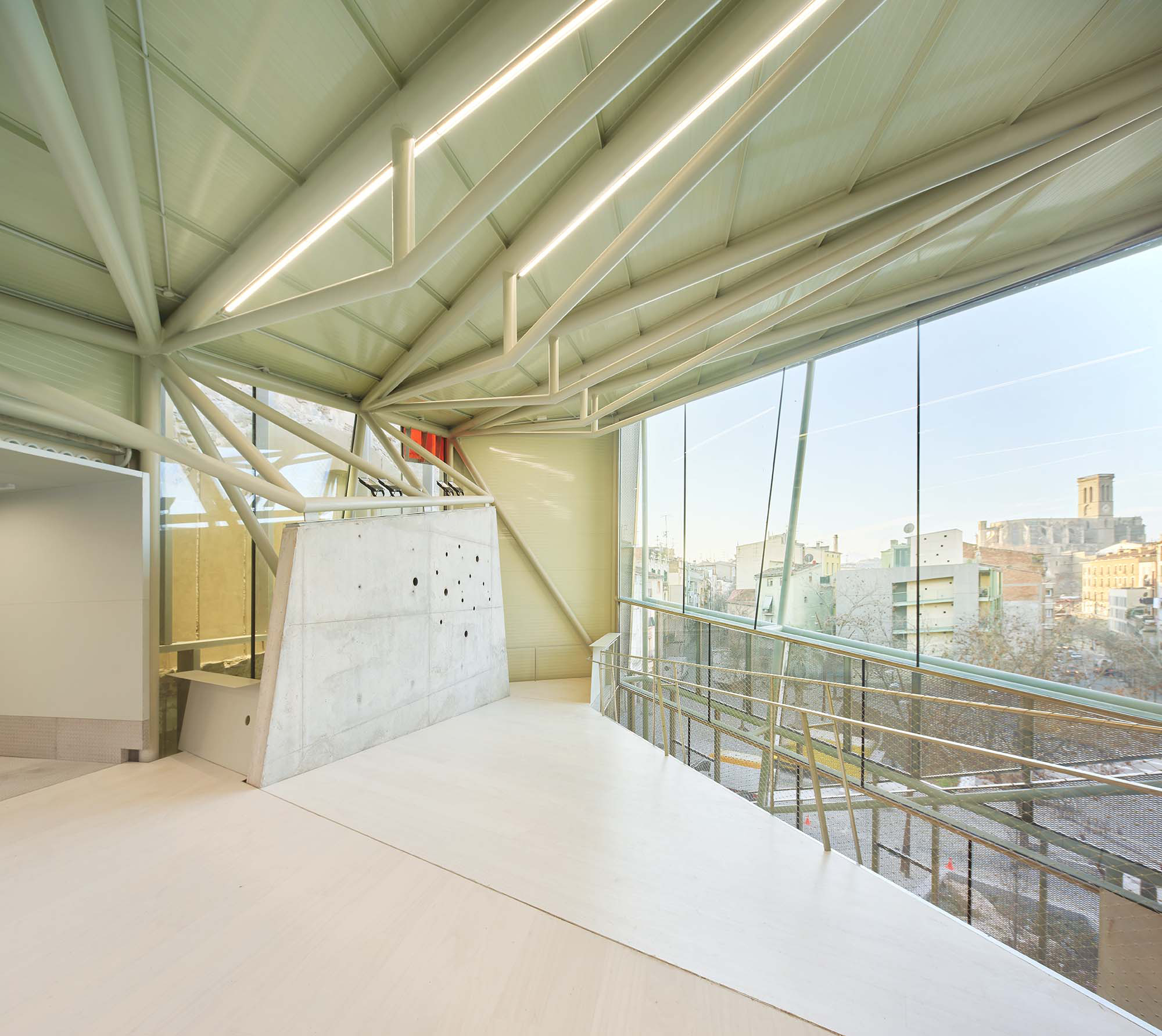
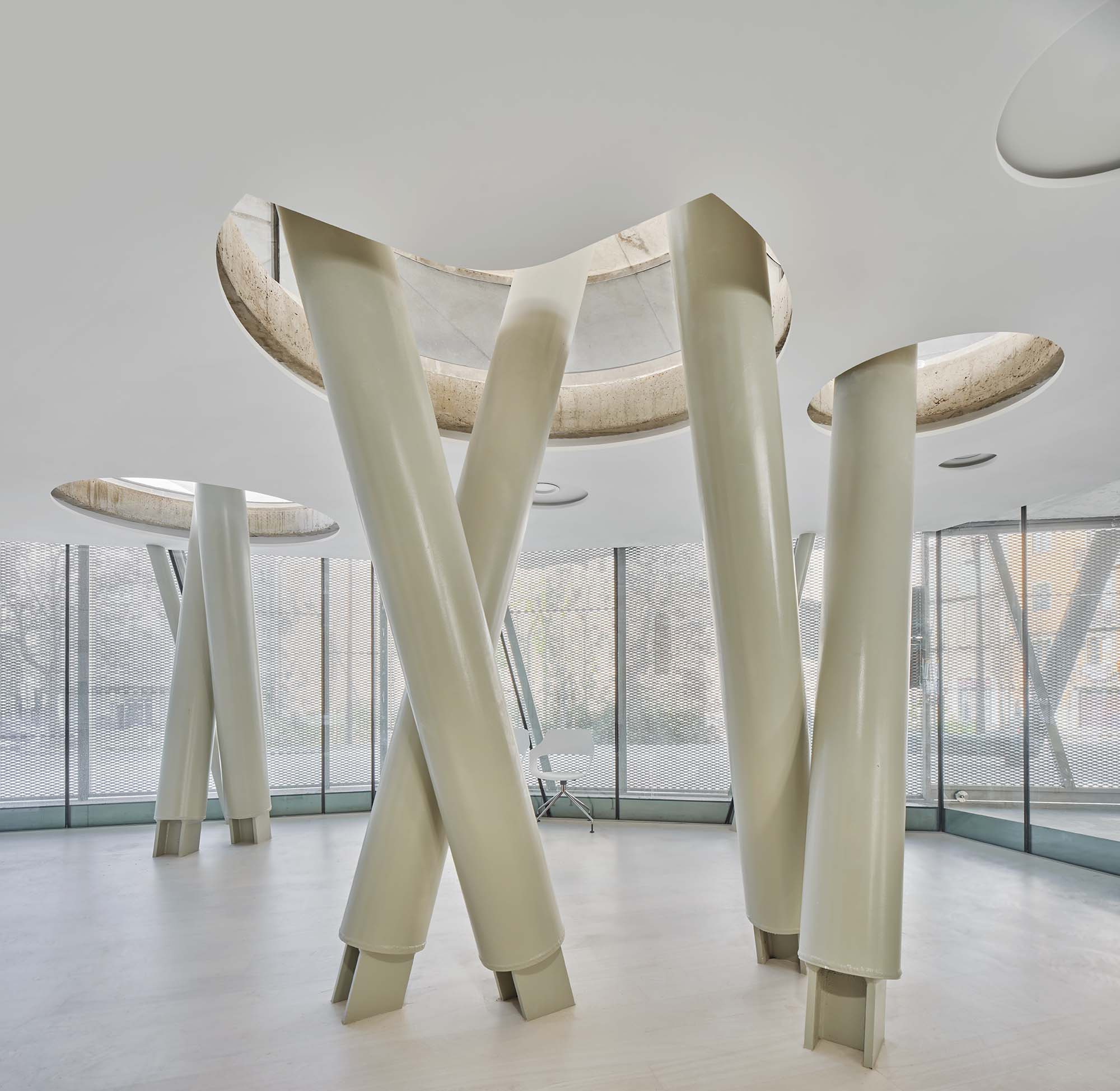
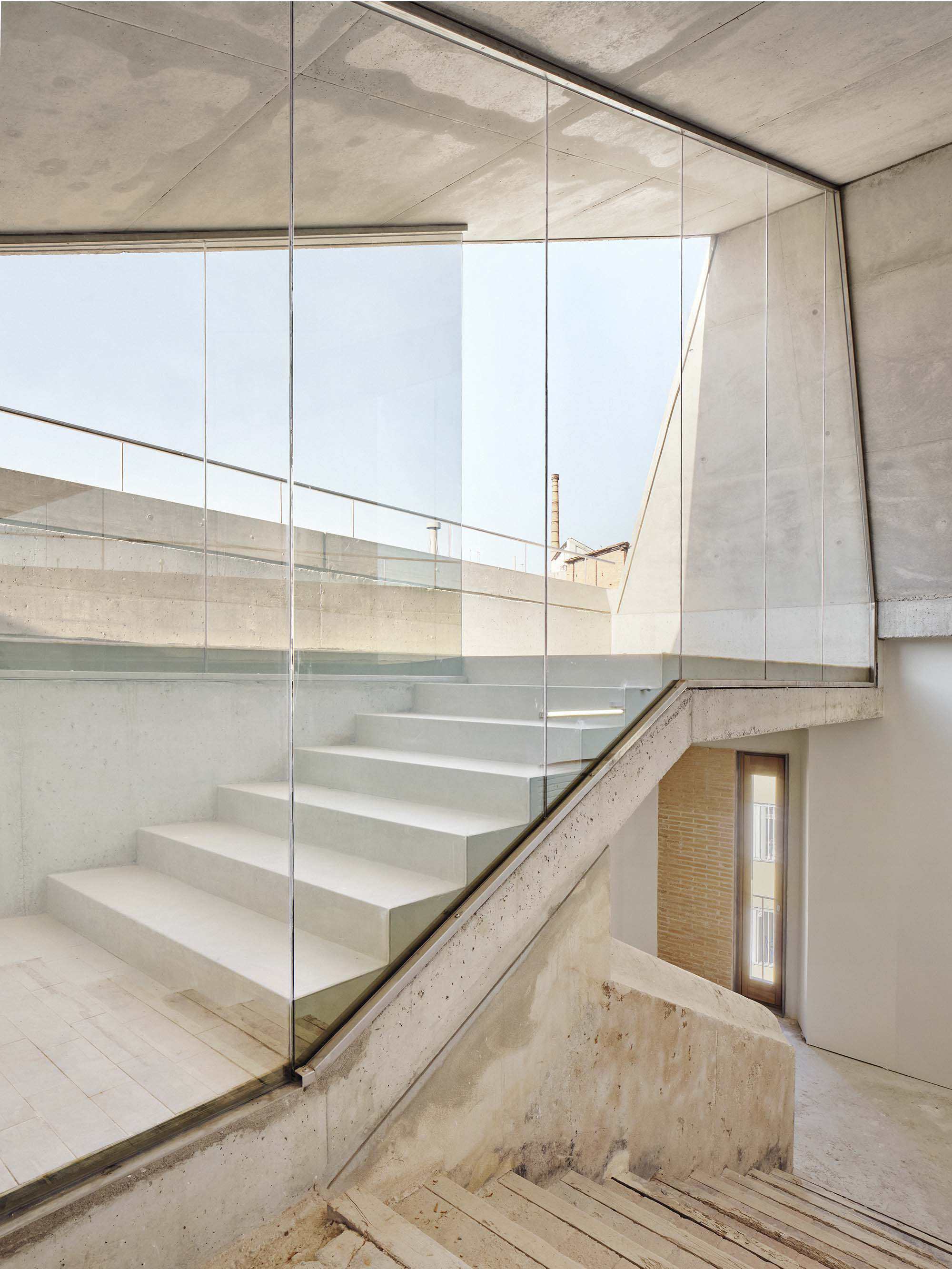
The intervention in the new accesses of the building pretends to be more than just a solution for the west façade of the old Jesuit college: the intervention proposes a new way of grasping both the building and its urban surroundings. The new accesses of the museum create a pathway which allows to admire the sights to the key elements of the old college (the cloister, the barrel vaults or the footprints onto the partitioning wall), sights over the adjacent urban spaces (Sant Ignasi’s Square and the urban orography of an old creek) and, finally, sights to the significant elements of the urban and landscape heritage of the city (the gothic basilica of La Seu, the defense tower of Santa Caterina or the mountain of Montserrat). The path created by the new accesses culminates, at its highest point, in a bleacher that overlooks the urban landscape.
The project, in short, aims to re-mean both the site of the intervention and the building itself by re-establishing links with the past of the Jesuit complex and with the city.