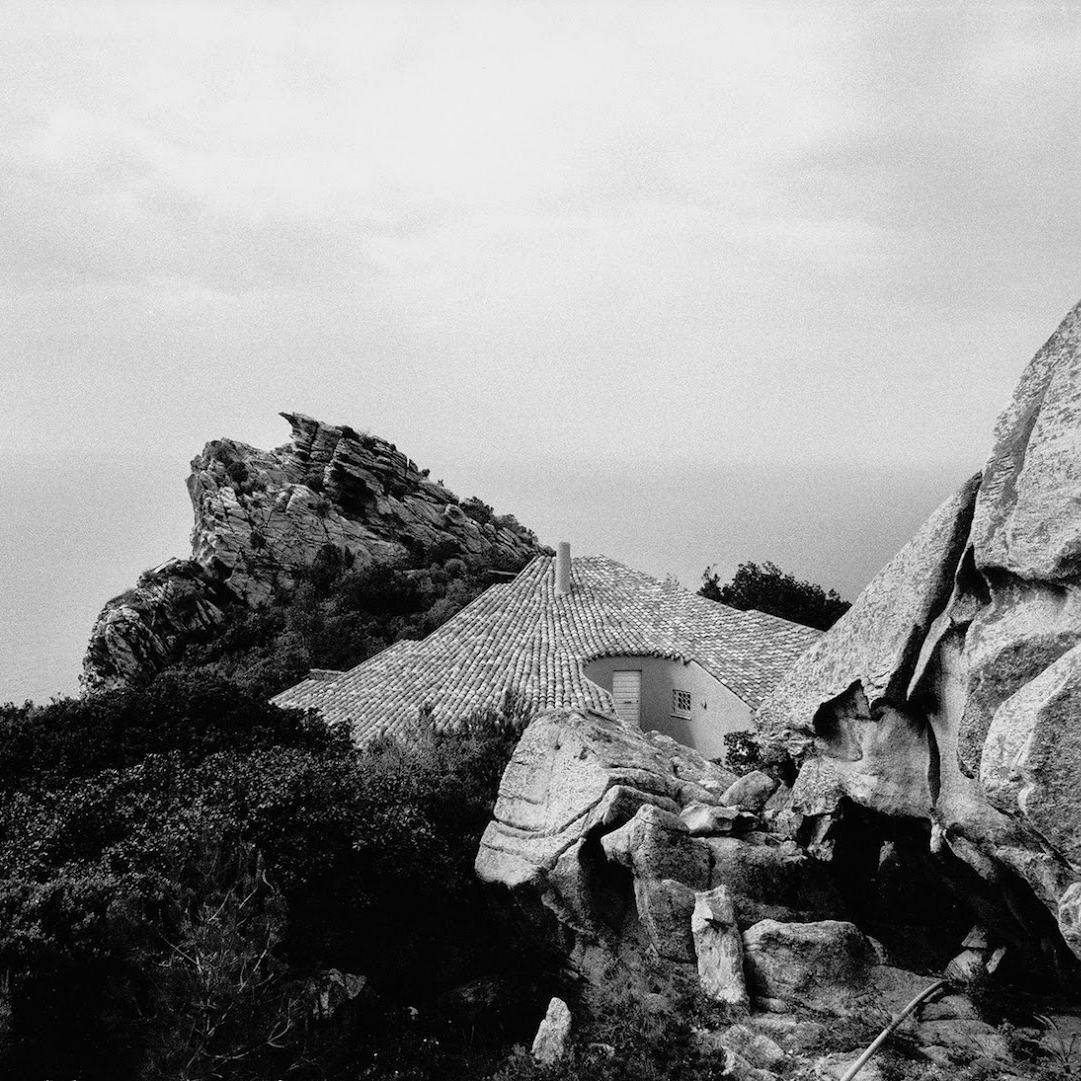
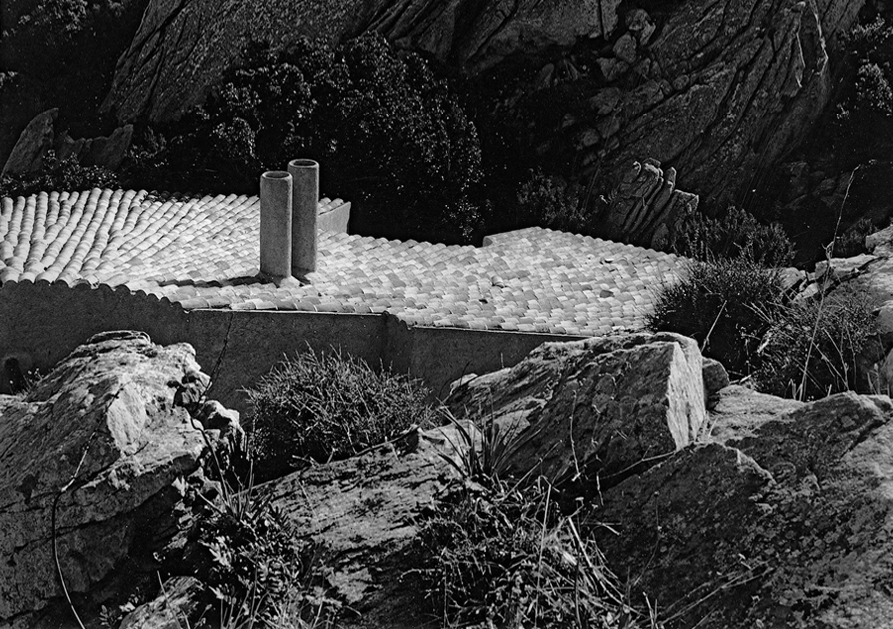
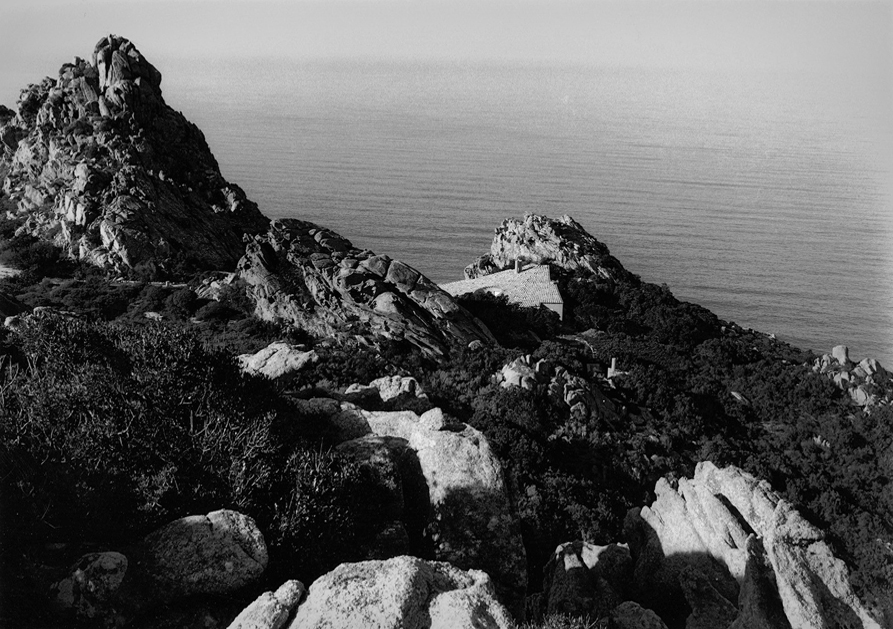
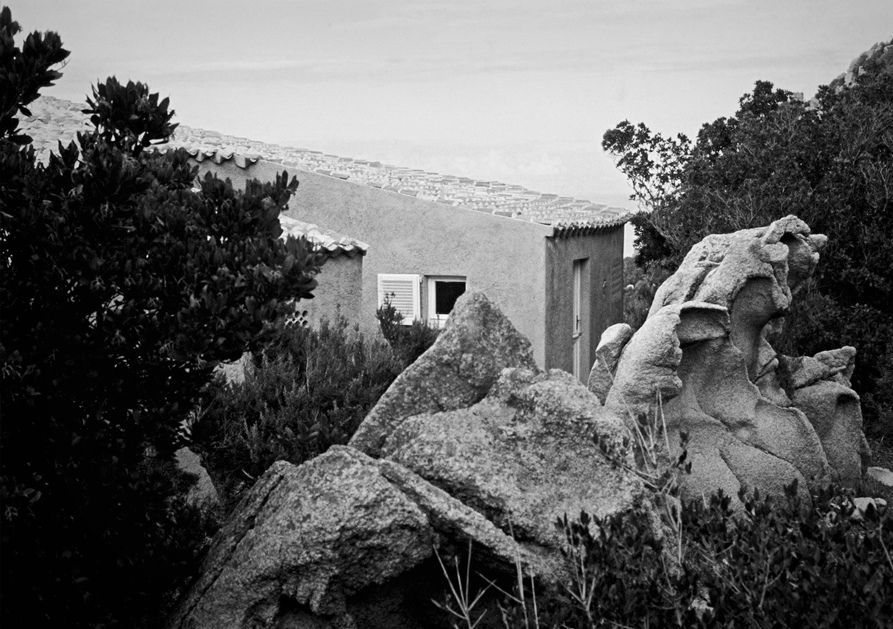
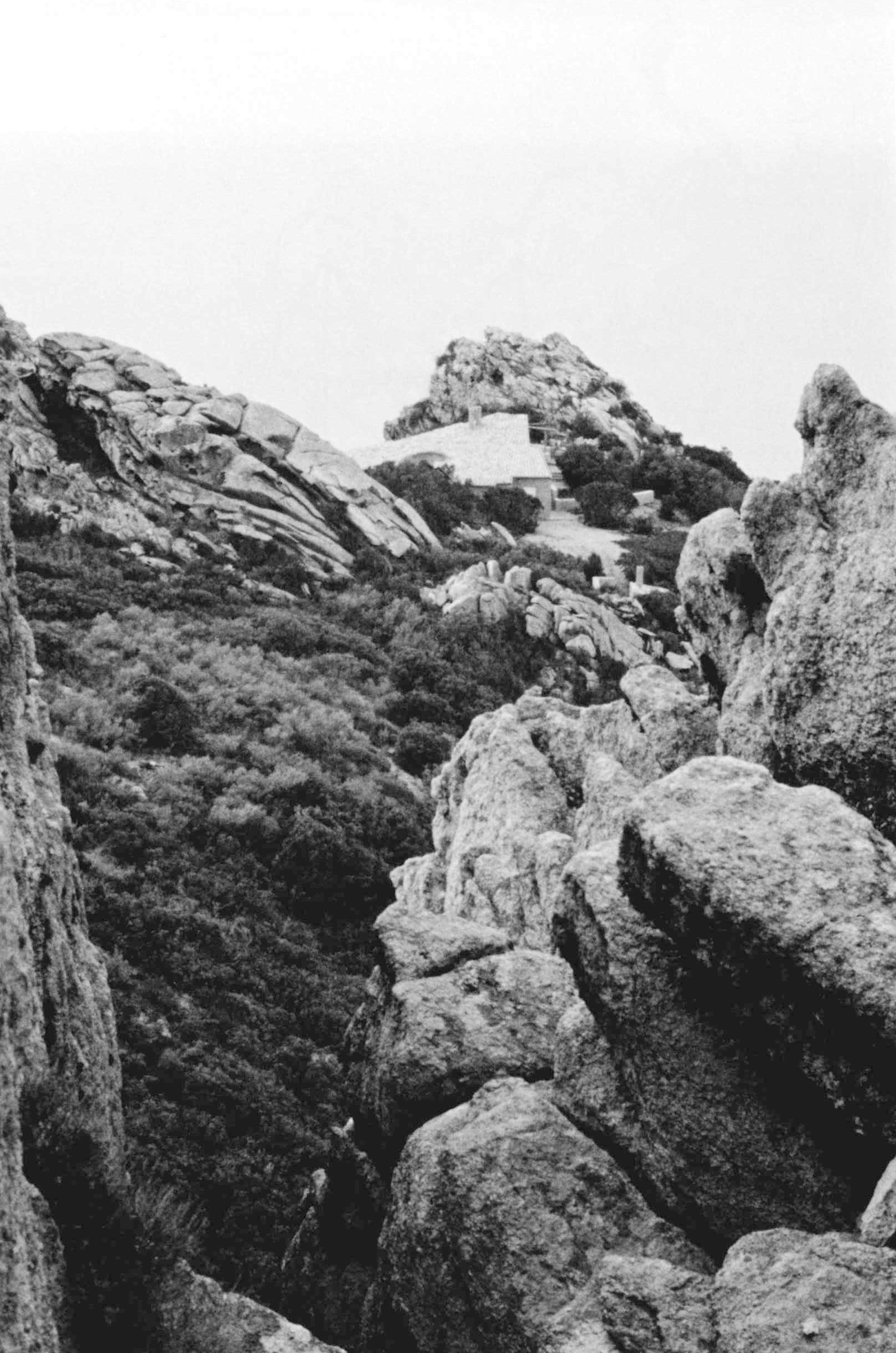
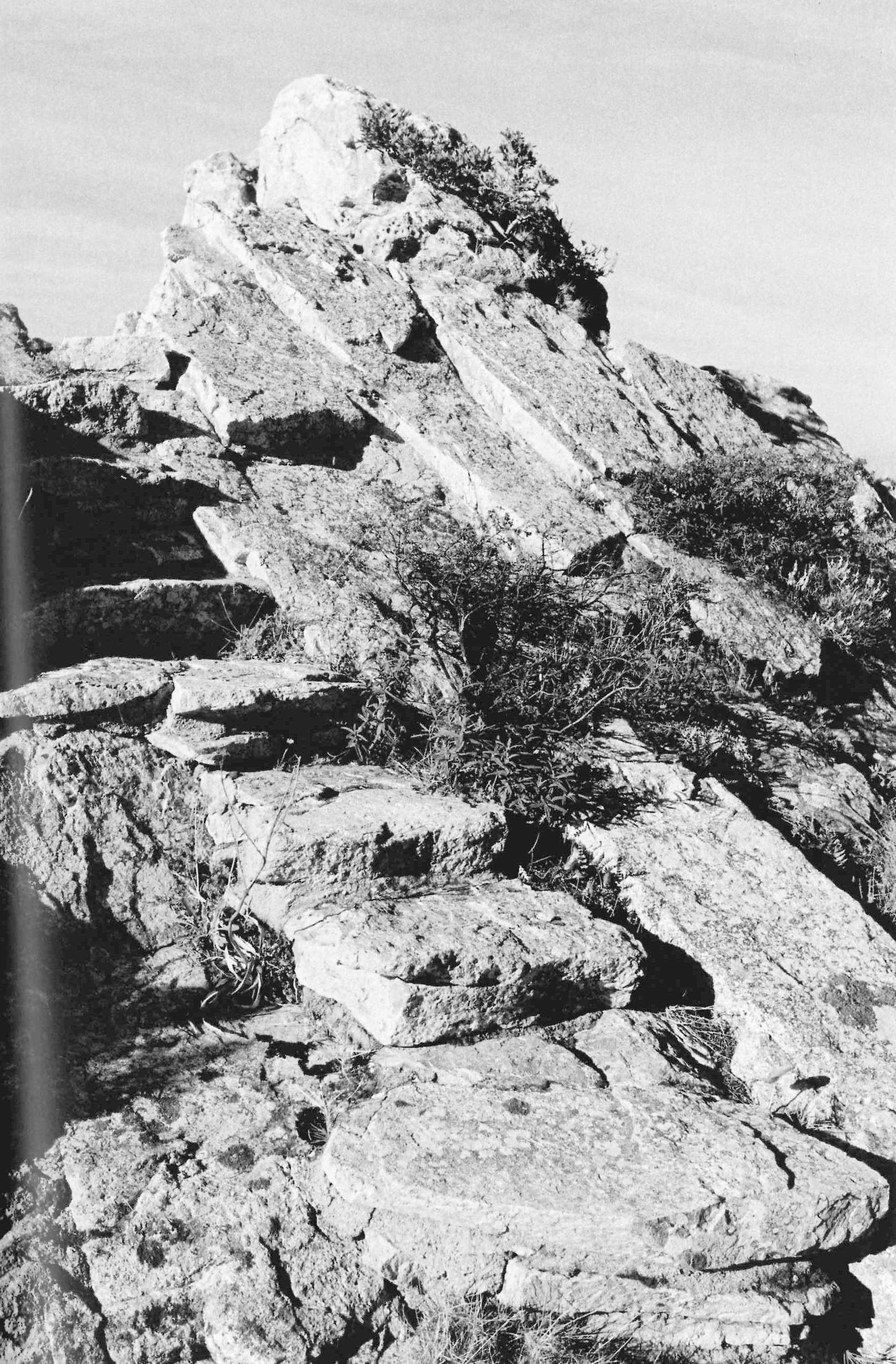
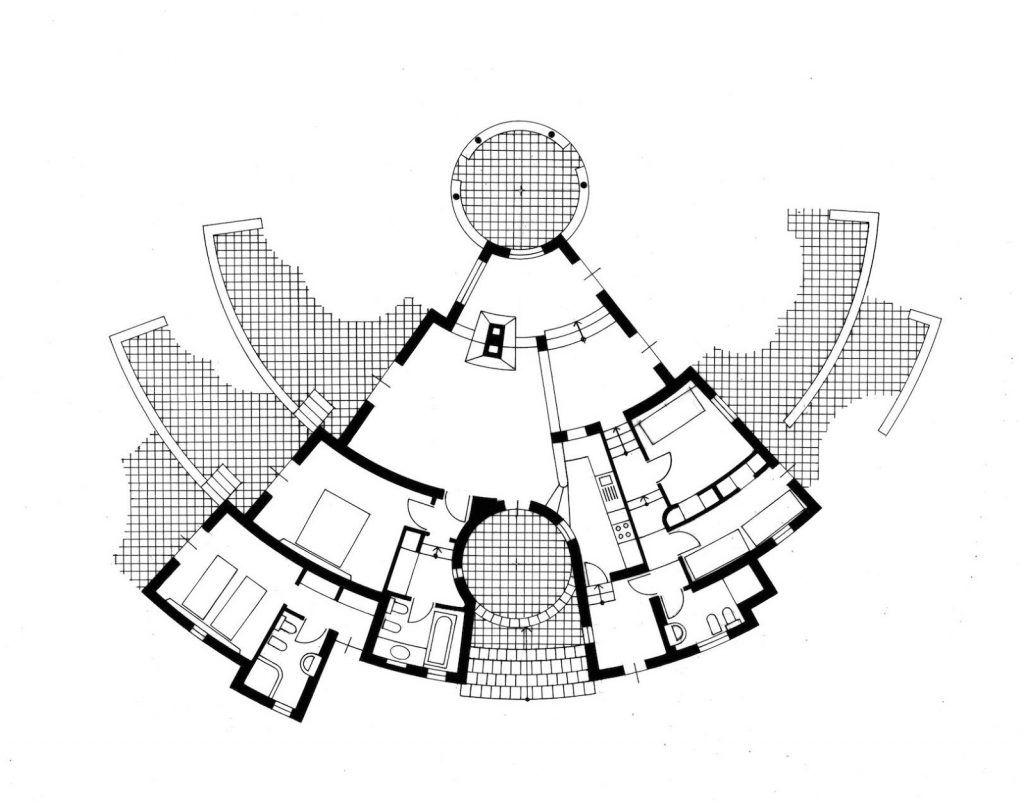
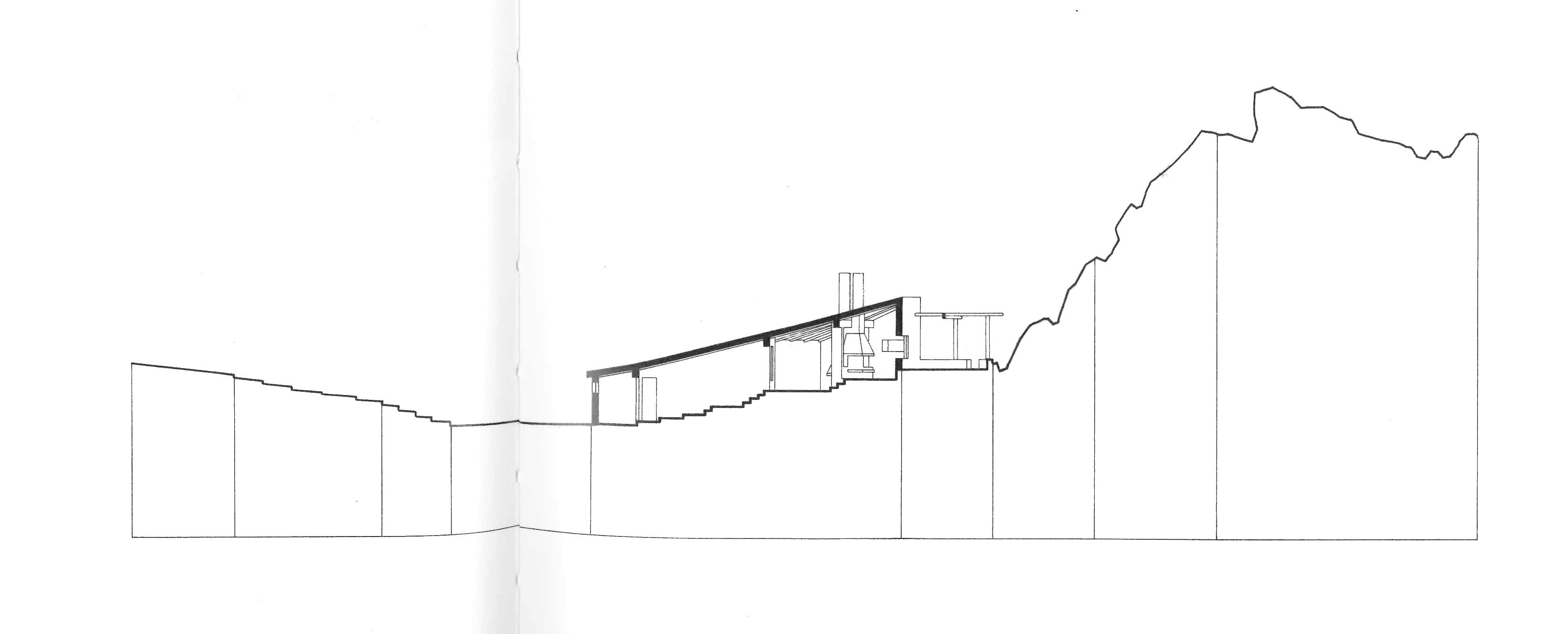
All the movement in the landscape of the Costa Paradiso, from the continuous ups and downs between the valleys to the dales, ridges, pinnacles and cliffs, tends to make visual orientation rather difficult, in part because the roads follow a logic that is quite different from the topography. It is possible for two houses to be just a few hundred metres apart but hidden from each other’s view, while the road that links them may be several kilometres long. Then, from around a corner, the sea emerges on the opposite side from the one where you left it just a few minutes ago, and even when the sea can be reached from these houses, you still need to tread warily over those sharp-edged rocks. And because the waves are often whipped up by the powerful mistral wind, you have to really want to go for a swim. There are few beaches and even fewer moorings. Many houses are equipped with mini swimming pools set back, high up on the hillside, like watchtowers drawing their water from the sea below.
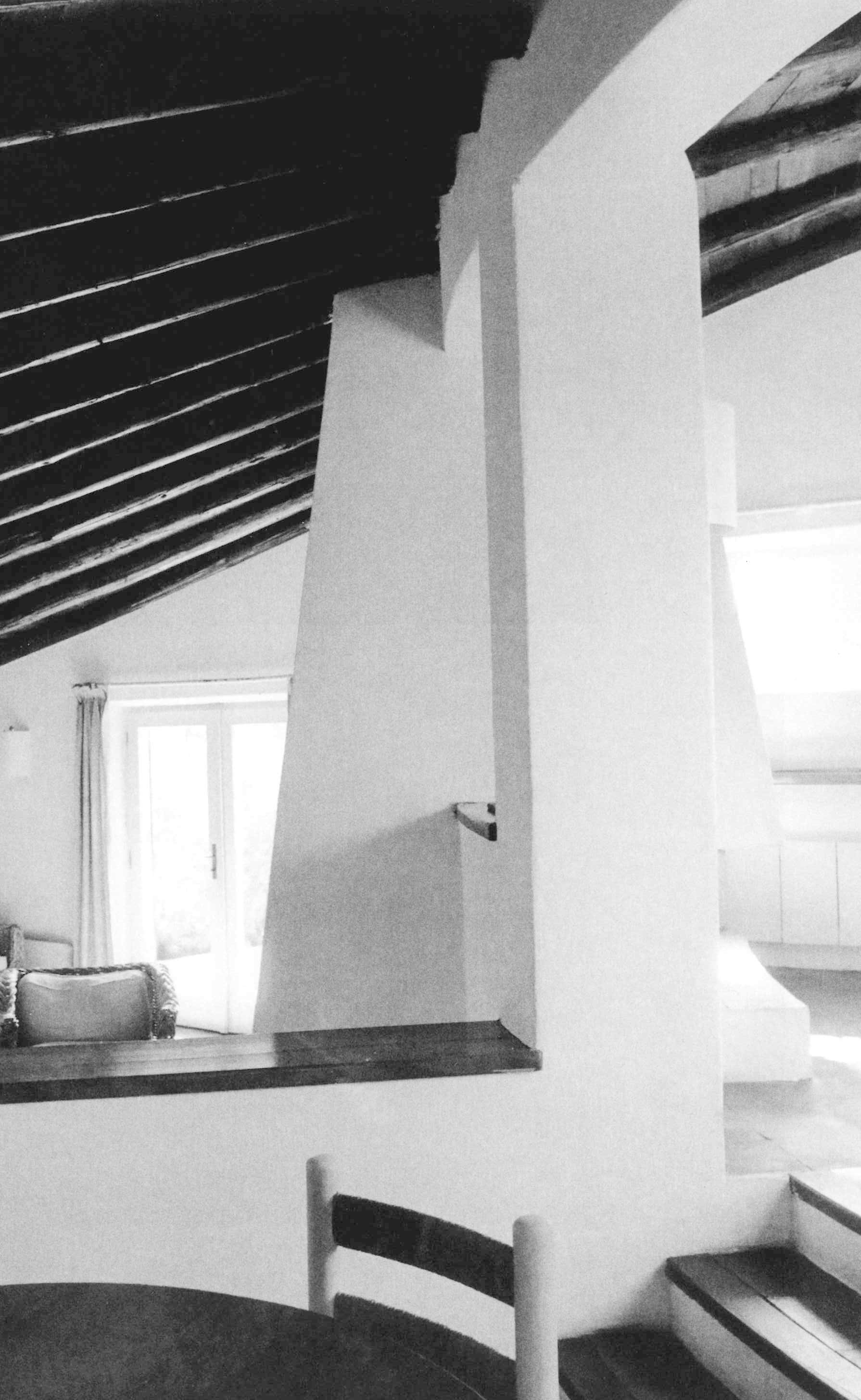
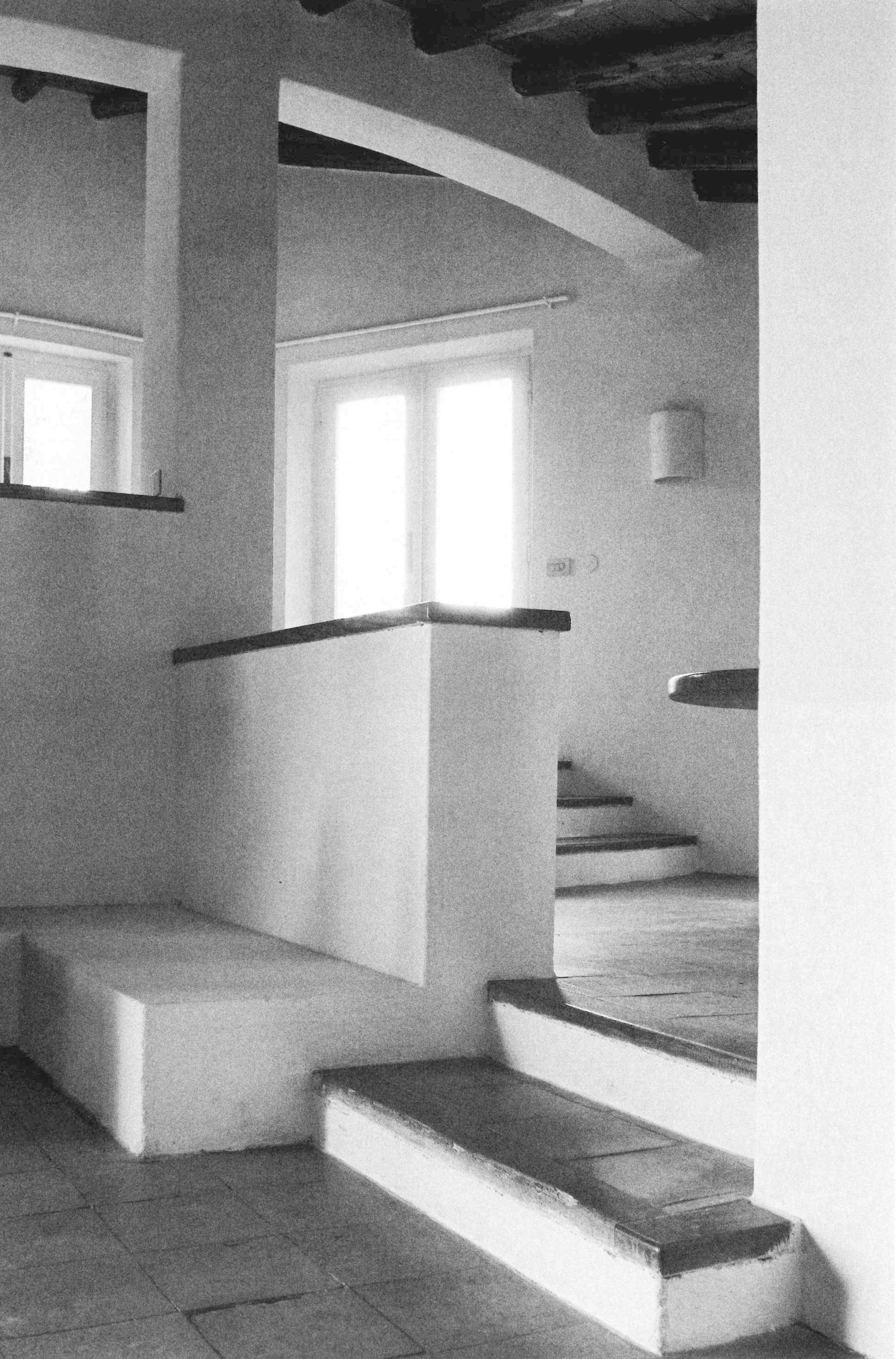
Casa Hartley actually occupies a dip in the ground between two of the pinnacles. The staircase of the house is deceptive, because in photographs it looks as if it were built on a large scale, but in reality, it is small. It is as if you had ended up on an Alpine pass with the land rising and falling away in all directions: it rises steeply towards the two juxtaposed pinnacles, rolls gently away towards the interior, and falls away sharply towards the sea. Ponis made a scientific study of the morphology of the land on which the house was to settle down as if on a bedsheet. The site is practically a miniature version of the wider landscape, and to study and conceptualise it required a host of different tools: walking over the ground in boots, carrying sketchbooks, making drawings, using photography – not to mention being able to view the site from close up and from a distance. The indigenous plants (whose trunks in Sardinia sometimes seem as old as the rocks themselves) formed part of his study, and by integrating them into the design as it was coming into being, Ponis anticipated and headed off the threat that in the future the owners might decide they wanted a little garden, flowerbeds, planters, a grassy lawn, irrigation systems, and non-native plants such as cactuses, oleanders, and bougainvillea.